XYCTF2025 Reverse 方向复现
CrackMe
ida 打开看到 WinMain 函数,同时注意到有一个 TlsCallback_0 函数
2
3
4
5
6>VOID NTAPI TlsCallback(PVOID DllHandle, DWORD dwReason, PVOID Reserved) {
//DllHandle:对于 exe 是进程句柄,对于 dll 是模块句柄;dwReason:回调原因;Reserved:保留参数,一般用不到
if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH) {
MessageBoxA(NULL, "TlsCallback Triggered!", "Info", 0);
}
>}
点进 WinMain,有反调试,先打断点运行起来用 ScyllaHide 去一下反调;很多传入了多个参数的 sub 函数点进去看发现没有什么重要信息,找到 sub_xxxAC00(v39),点进去后同样注意到 v6 = sub_7FF7AD959470;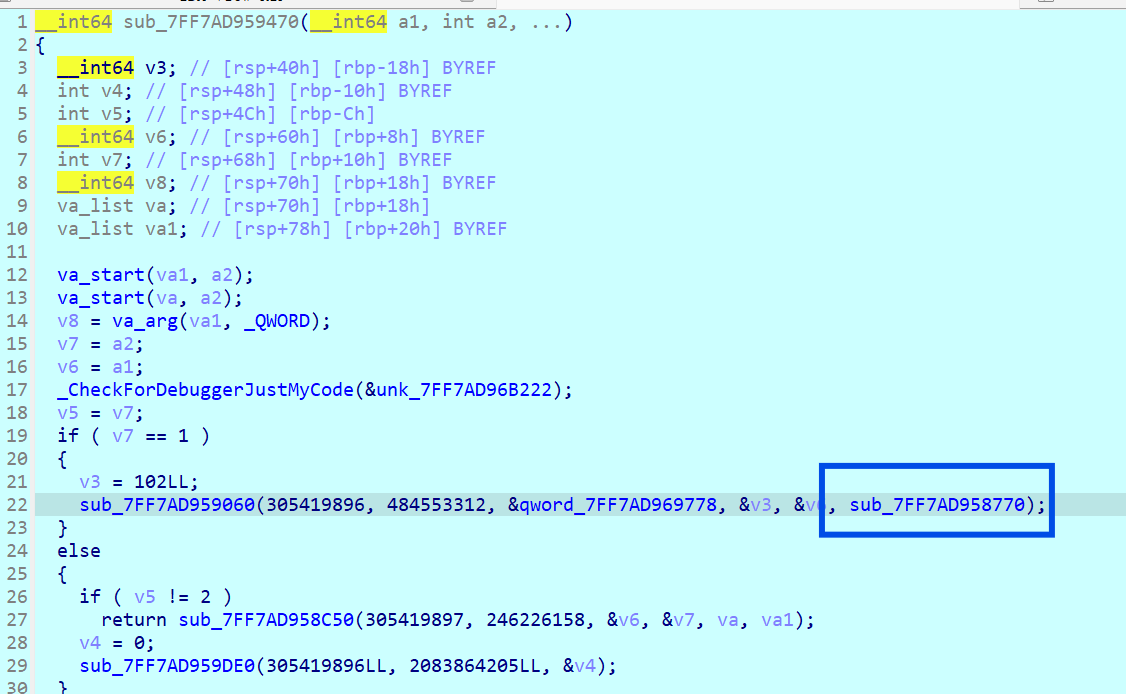
sub_xxx8770 里面像是一个消息处理器,根据不同的参数值分发不同的处理逻辑
而 Tlscallback 这边,进入 sub_xxx2370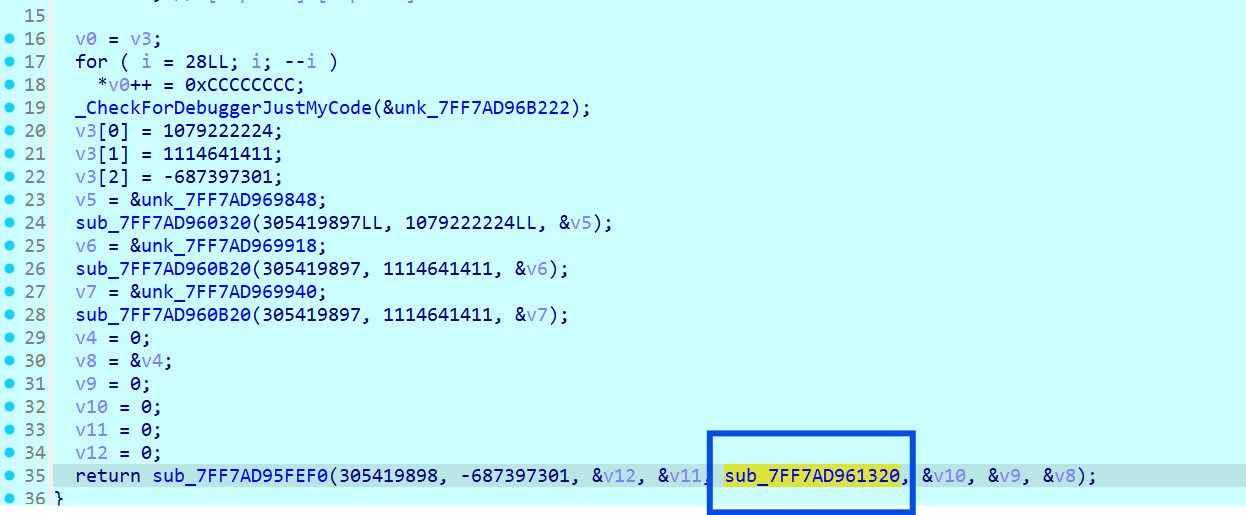
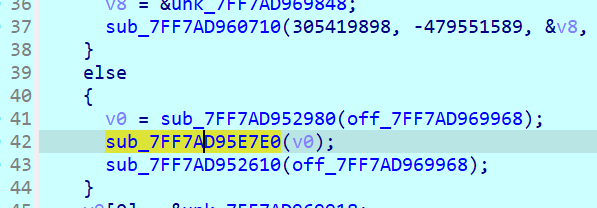
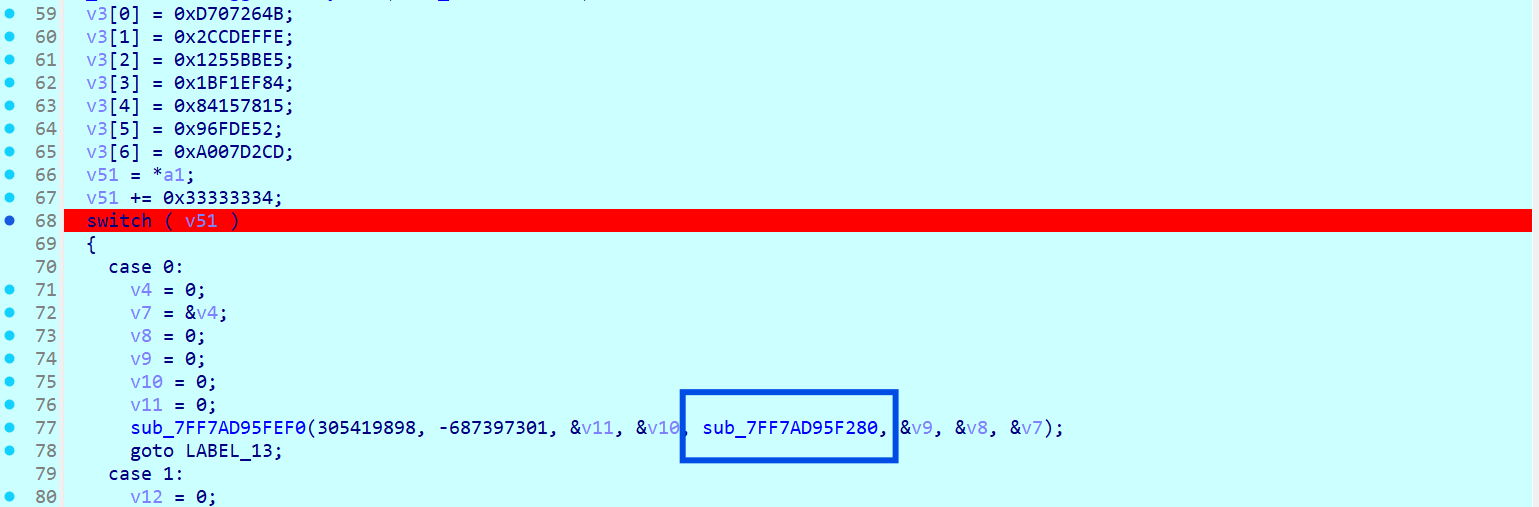
switch 下有五个 case,分别对应不同的参数,case0 里面带点进 sub_xxxF280 挺复杂的,留到后面看,case1、case2、case3 没什么东西,case4 和 case5 有可疑的函数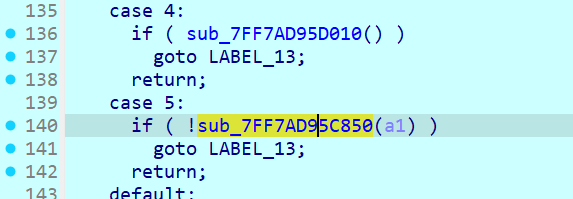
case4 的 sub_xxxD010 里面有个异或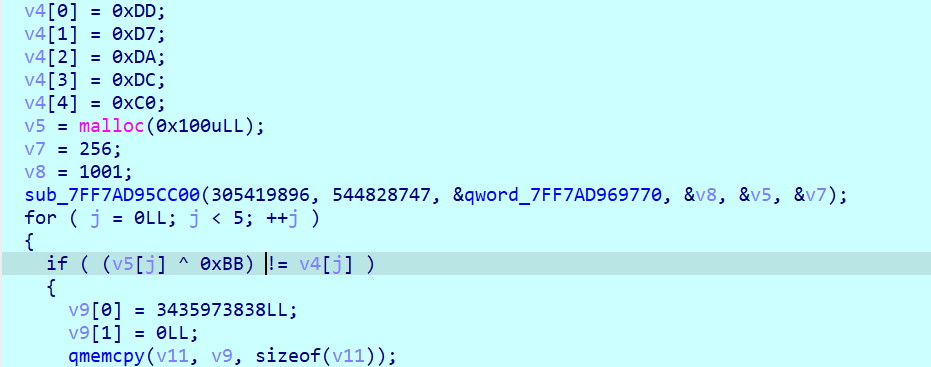
1 | |
解出来是 flag{,由此可知此处是校验 flag 的格式
case5 的 sub_xxxC850 里看到了 CRC 校验
爆破出输入
1 | |
所以这里得到部分flag moshui_
case0 的 sub_xxxF280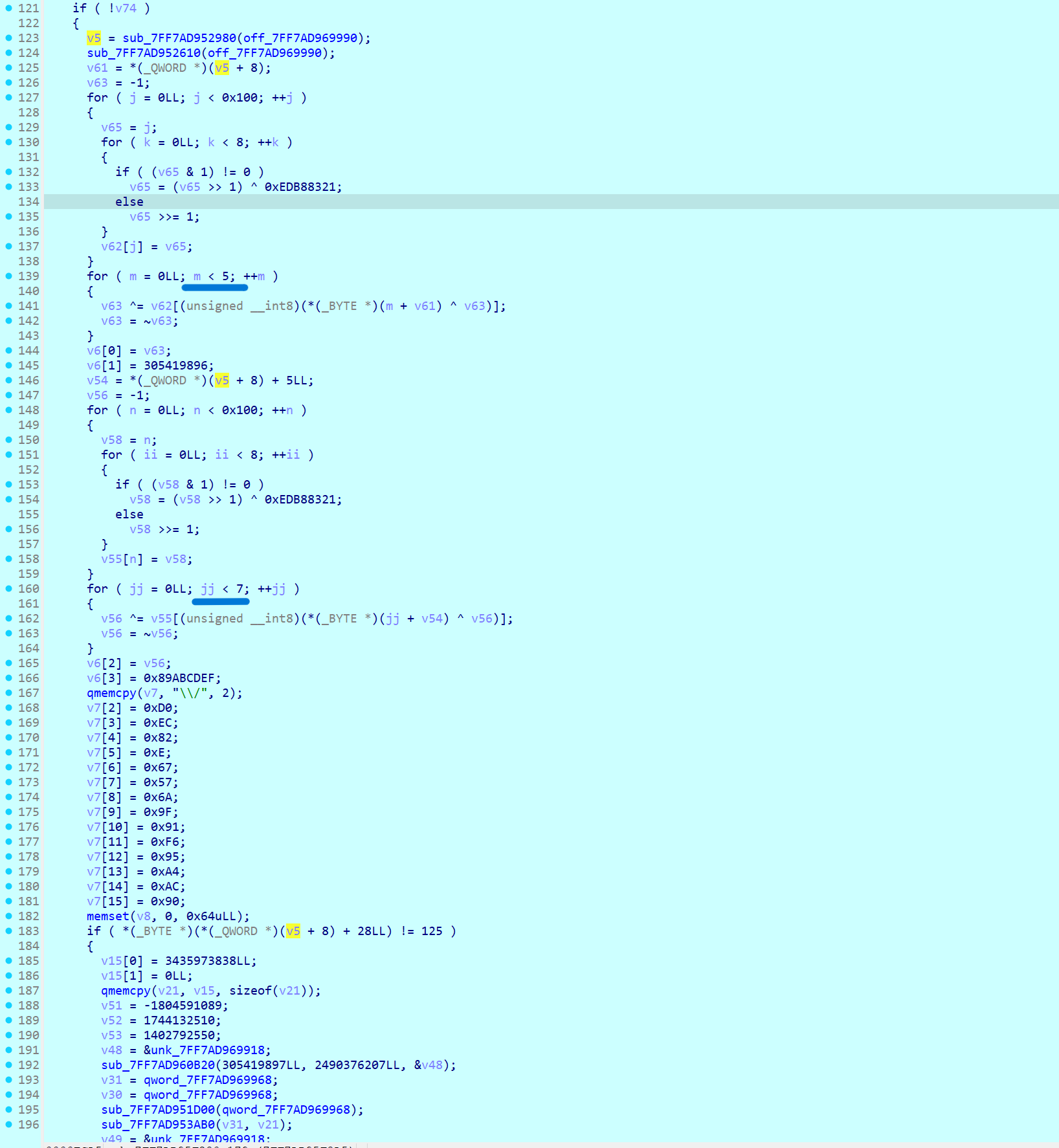
里面依旧有 crc ,不过这里的 crc 不是进行校验,而是使用输入的前 5 个字节(“flag{“)加上 {} 内部的前 7 个字节(v7 数组里面)生成了两个四字节的密钥(v6[0]和v6[2]),再加上另外连个直接赋值的即可得到完整密钥
1 | |
密钥 :0x42b2986c,0x12345678,0xe40ecf0a,0x89abcdef
同时在里面发现sub_xxx1500sub_7FF7AD961500(v6, *(_QWORD *)(v5 + 8) + 12LL, 16LL, v8);
分析后可知 a1 传入的是原始密钥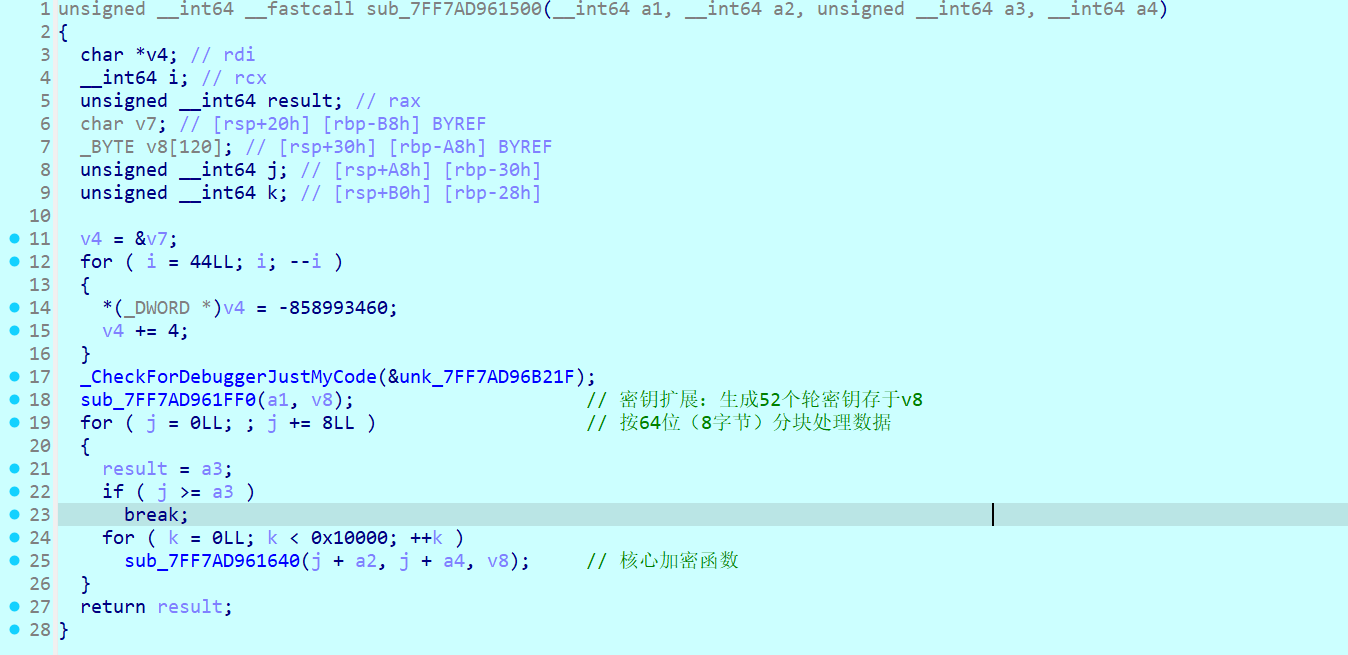
sub_xxx1FF0 :将128位原始密钥扩展为52个16位轮密钥(符合IDEA标准)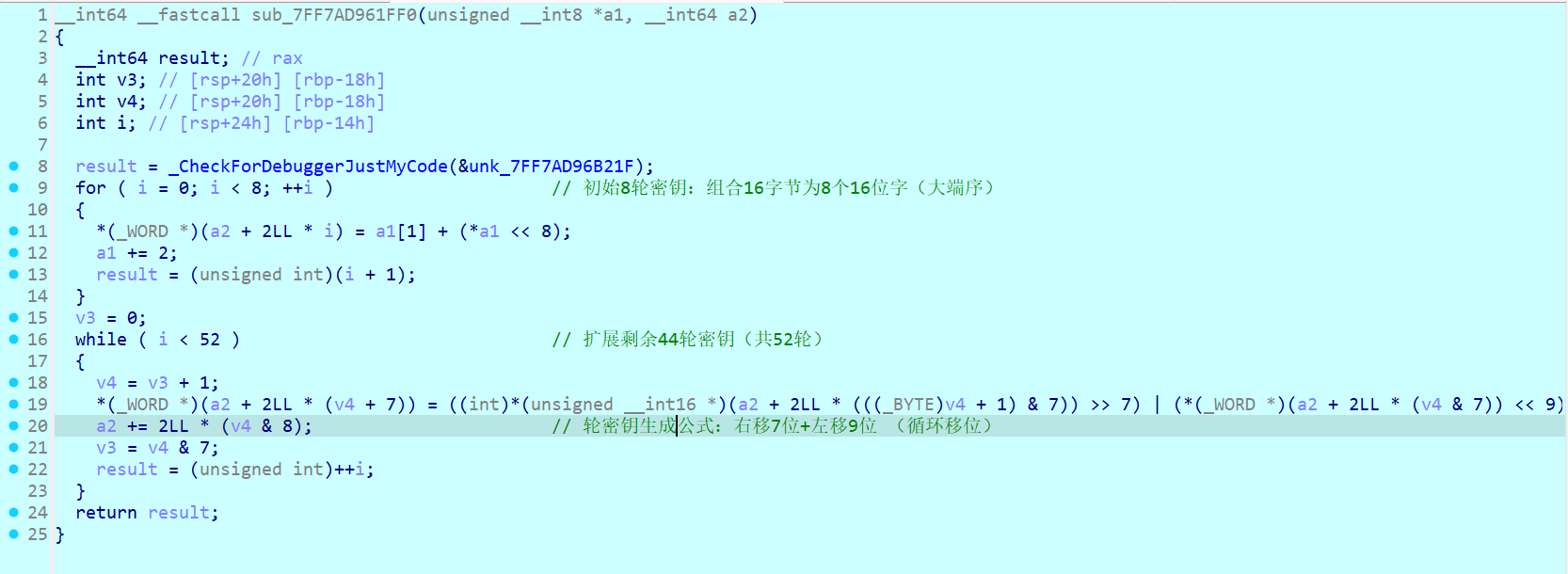
sub_xxx1640 :IDEA 加密
分组长度:64 位
密钥长度:128 位
共 8 轮 + 1 次输出变换
每轮用到了三种不同的运算:
模 2¹⁶ 加法(模加)
模 2¹⁶ + 1 乘法(模乘)
按位异或 XOR
主要特点包括使用模乘(模65537)和模加(模65536)运算,以及大量的异或操作
1 | |
密文在 v7 数组中: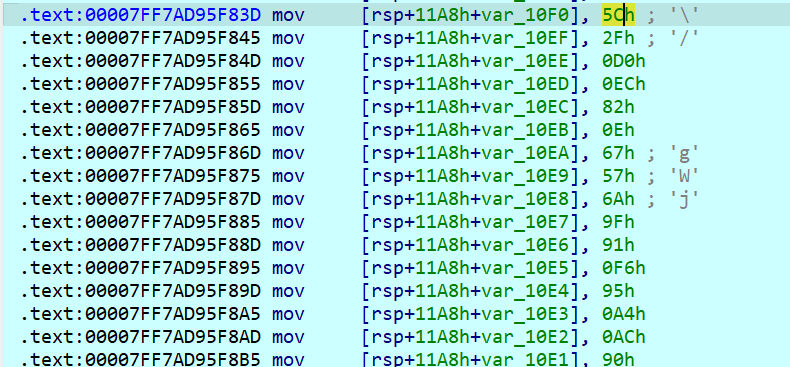
解出第二部分:
1 | |
所以第一部分的 moshui_ 和第二部分的 build_this_block 拼接起来就是完整的 flag{moshui_build_this_block}
Dragon
附件是一个 .bc 文件,用 file Dragon.bc 查看文件类型
得到Dragon.bc: LLVM IR bitcode
继续往下编译 clang Dragon.bc -o Dragon
然后 ida 打开编译好的 Dragon 文件,main 函数
读取输入后进入一个加密函数(CRC 64),最后又字符串比较,动调提取出密文
1 | |
密文有 96 字节 -> 12 个 64 位整数,每两个字符为一组,生成一个 64 位的 CRC 值,与密文对比
因此可以得出输入是 24 个字符,需要爆破 12 组的 2 字符组合
加密函数
1 | |
解密脚本:
1 | |
flag 为flag{LLVM_1s_Fun_Ri9h7?}
WARMUP
附件是一个 .vbs 文件,是一种包含用Visual Basic Scripting Edition编写的脚本代码的文本文件,不需要编译,直接由Windows Script Host (WSH)解释执行
在网上看到相关处理方式是:用 vscode 或者 其他文本编辑器打开,把开头的 Execute 改为 wscript.echo
直接运行即可得到源代码
Execute 是用来执行代码
wscript.echo 的作用是将一个或多个字符串作为输出打印到控制台(或者在图形界面中弹出一个对话框)
运行后果然看到了源代码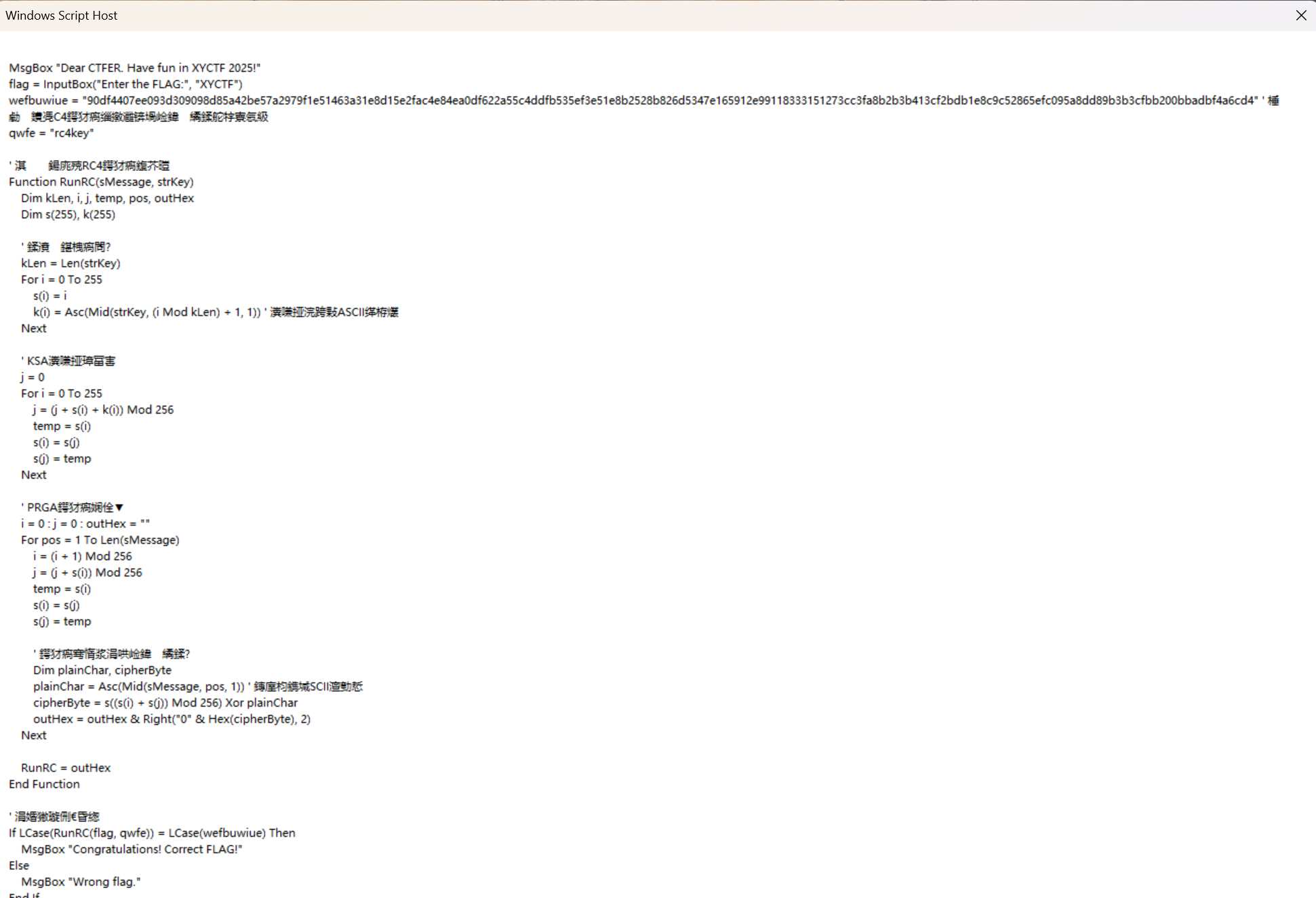
不难看出这是一个标准的 rc4 ,
密文是 “90df4407ee093d309098d85a42be57a2979f1e51463a31e8d15e2fac4e84ea0df622a55c4ddfb535ef3e51e8b2528b826d5347e165912e99118333151273cc3fa8b2b3b413cf2bdb1e8c9c52865efc095a8dd89b3b3cfbb200bbadbf4a6cd4”
密钥是
“rc4key”
解密脚本
1 | |
题目中说 flag为flag{}包含的内容进行md5加密并用XYCTF{}包含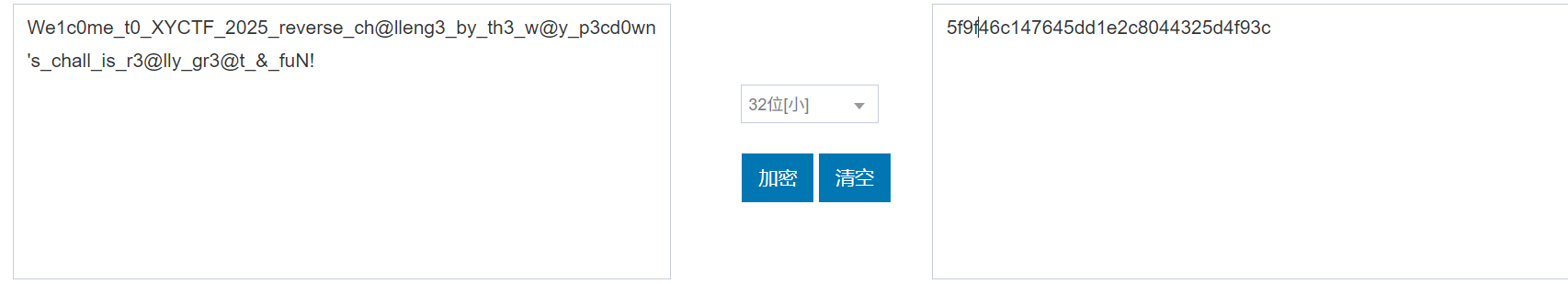
所以最终的 flag 为 XYCTF{5f9f46c147645dd1e2c8044325d4f93c}
Lake
静态看一堆 sub,于是打断点动调找函数逻辑,调试时发现了一个可疑的函数 sub_100001B70
前面有好几个do while 循环,这是在打印题目叙述部分
打印结束后读取输入并对输入做了一些处理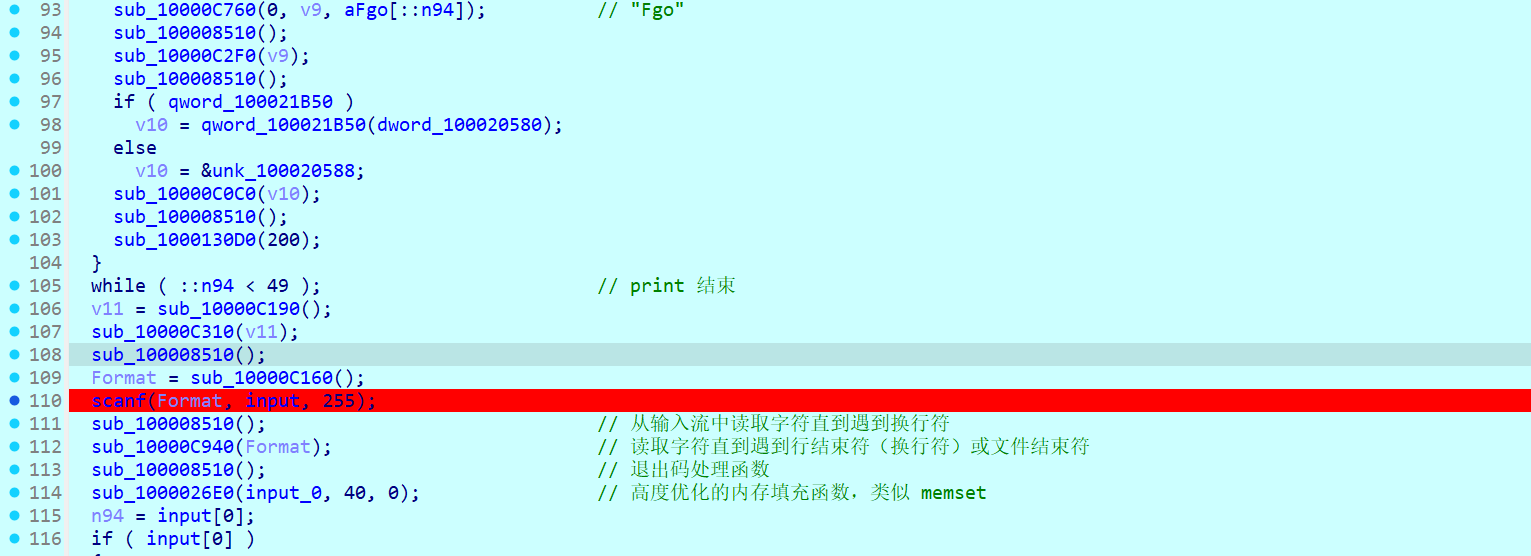
然后进入一个 switch case ,这是一个小的 vm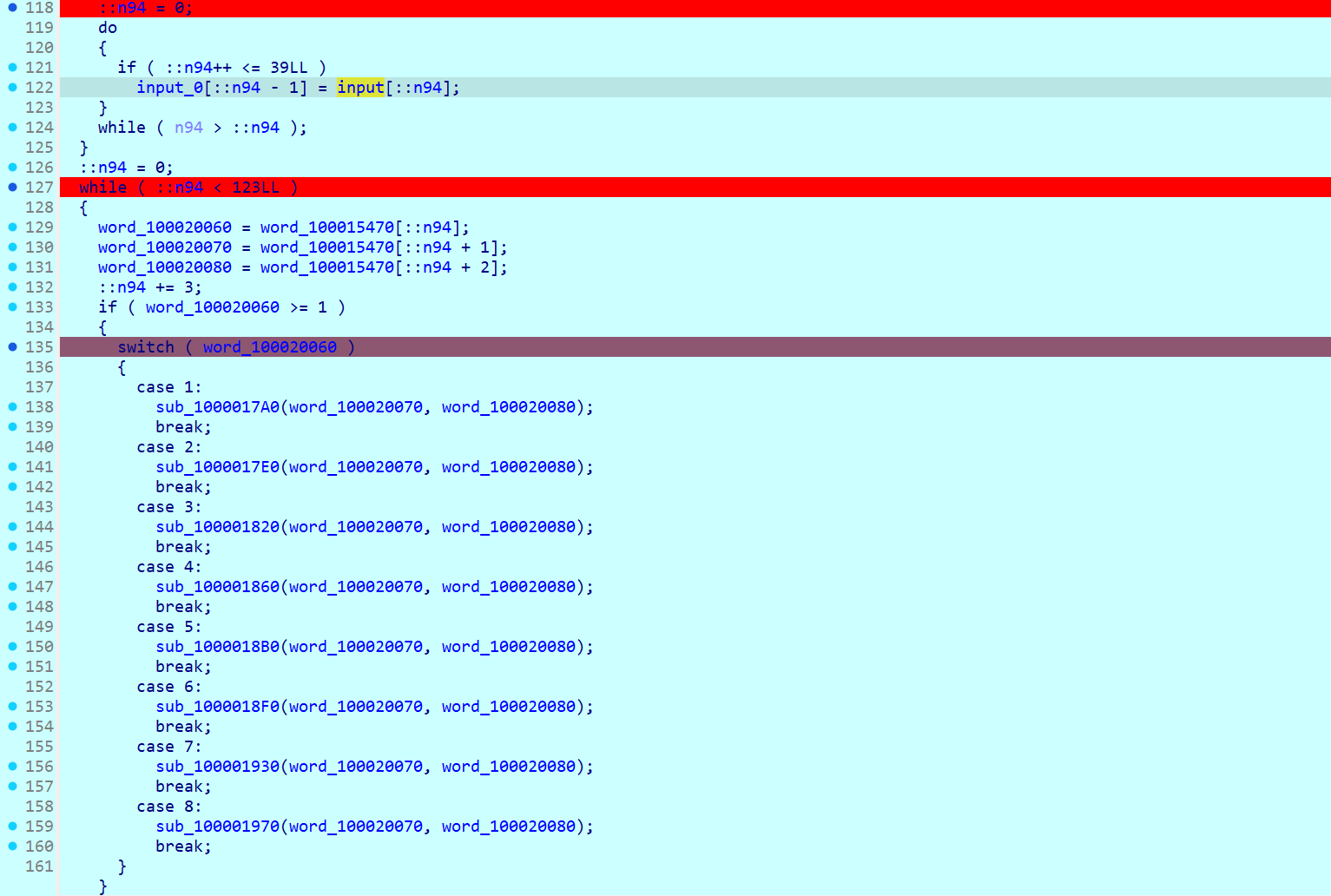
操作码在 word_100015470,长度为 3 个字节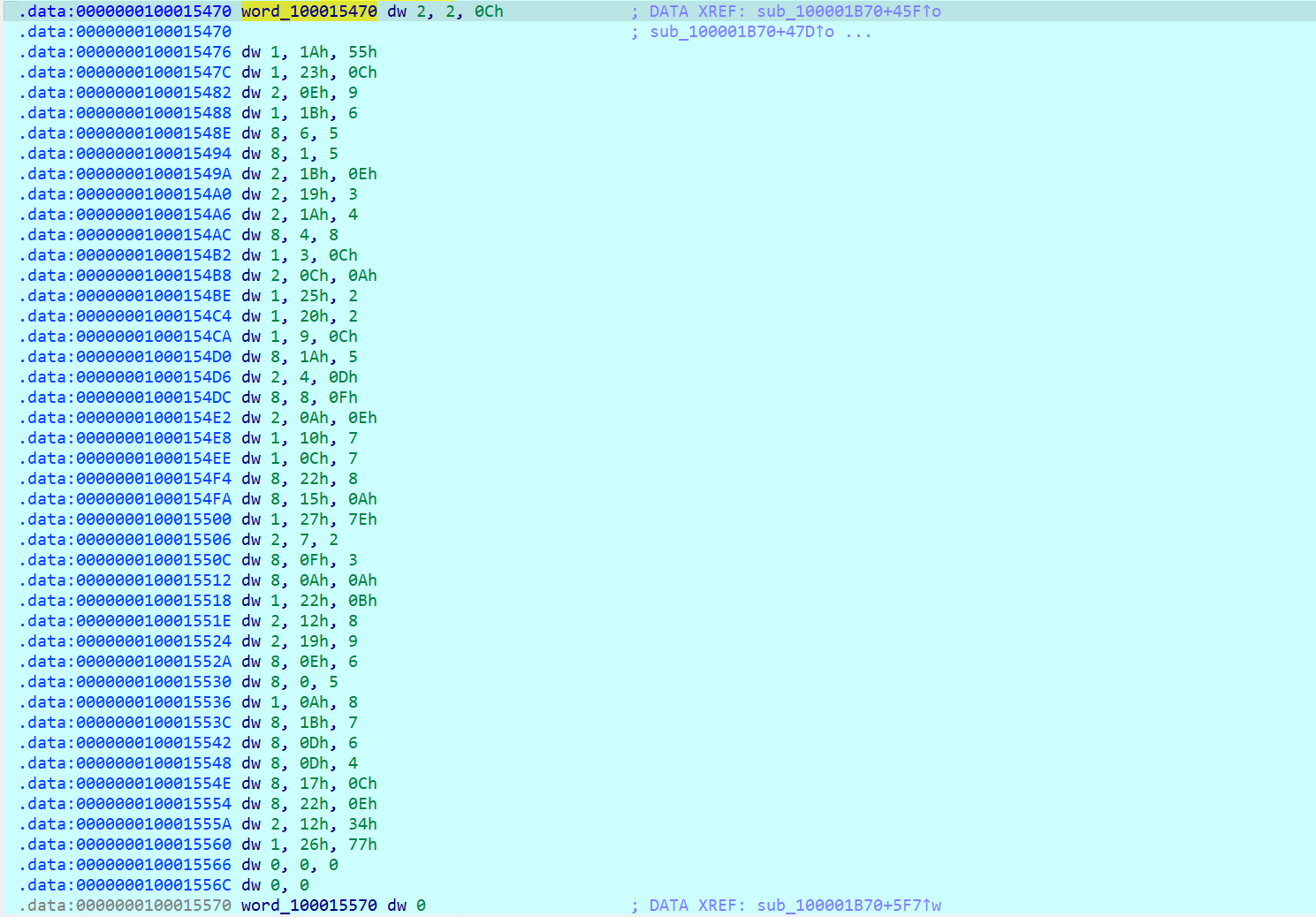
每个 case 点进去都对应一个操作,三字节一组的opcode,第一个数是 case 的情况,第二个是 input 的索引值 index,第三个是操作数,从 opcode 就可以看出其实涉及到的 case 就只有三个,case 1、case 2 和 case 8,分别对应的操作是 加法、减法和异或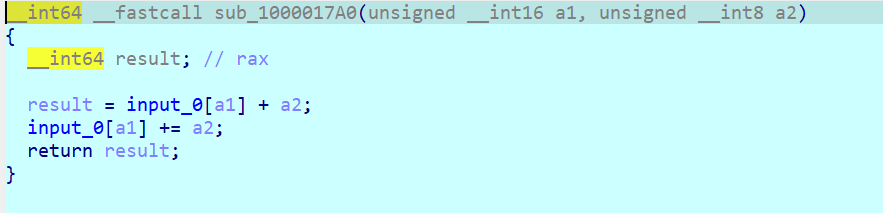
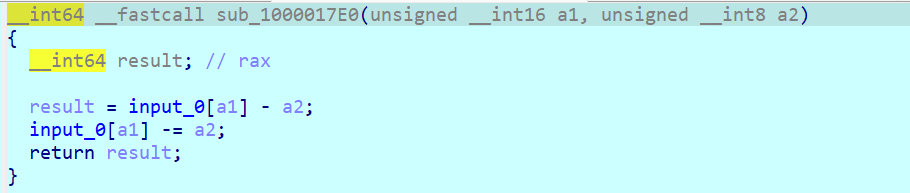
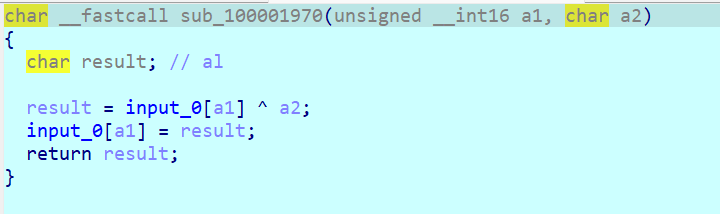
再往下走是一个加密和比较,比较之后同开始一样是输出一些字符串
比较处找到密文,一共 40 字节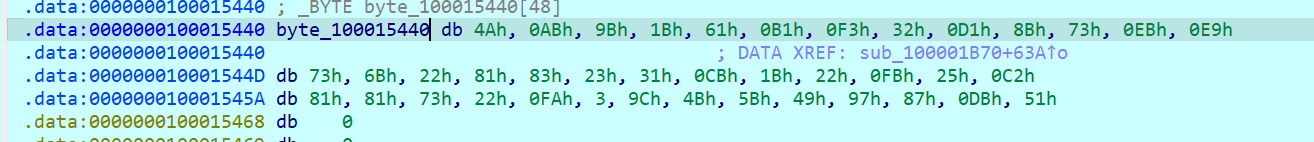
然后看加密部分,是一个循环移位,把密文分成 10 组,每组 4 字节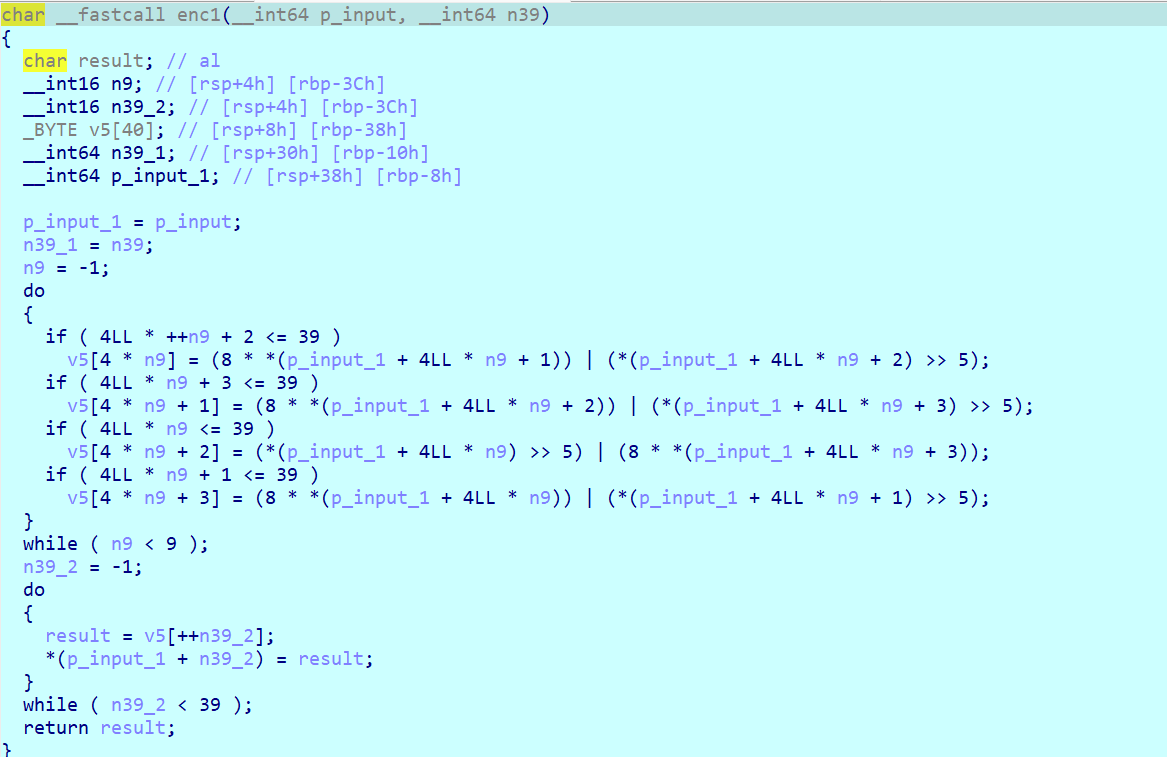
简化一下它的逻辑
1 | |
解密 enc1
1 | |
得到中间结果 ciUsfL6>}z1nd].mf00d_ycd0$\xb8P@nd_i3\x89kj2\xf0\xfb
接下来看那个小型 vm,整理之后如下
1 | |
打印出它的过程
1 | |
然后进行简单的逆向
1 | |
所以最终的 flag 为 flag{L3@rn1ng_1n_0ld_sch00l_@nd_g3t_j0y}
moon
pyd 逆向,扔 ida 之后不难发现这是 python 3.11 写的,所以做题也用相同的 python 版本
这次发现了一个很奇妙的方法来做 pyd 的题
附件的 main.py
1 | |
然后可以在这里面添加一行 help(moon)
运行 main.py,就可以得到很多有用的信息
1 | |
从这里就可以直接看到关键函数和关键数据,TARGET_HEX 是密文,xor_crypt 是加密函数,而其中传入的 seed_value 应该就是下面的 SEED
因此直接修改 main.py
1 | |
运行发现有报错,TARGET_HEX 是一个字符串,需要转换成字节数据
稍作修改
1 | |
直接运行打印出 flag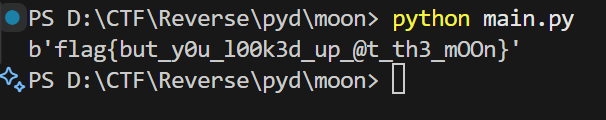
flag 即为 flag{but_y0u_l00k3d_up_@t_th3_mOOn}
除了这种做法外,我依旧尝试了之前的方法
main.py 中加个 import os 和 print(os.getpid()),以便 ida attach 到 process 进行动调
frida hook 脚本
1 | |
js 脚本
1 | |
trace 出来的只有两种,一个是 PyObject_RichCompare,一个是 PyNumber_Xor
这里有个注意的地方只有在输入长度正确的时候它才能够完整输出所有的异或,否则 trace 出来的 xor 的数量是不准确的,而字符串长度我自己做的时候没找出来,后来看到 liv 师傅的 wp 之后才发现输入的长度需要满足 35 字节长度
密文的话在 ida 中 string 窗口不难发现426b87abd0ceaa3c58761bbb0172606dd8ab064491a2a76af9a93e1ae56fa84206a2f7
trace 结果截取出 Xor 的部分
1 | |
解密脚本
1 | |
EzObf
找到 main 函数,跟进看到 main_0,发现被混淆了
1 | |
这后面也是一大片未识别成代码的数据,动调 f7 步进
可以这之后也一直都是这个结构
把真实指令藏在 popfq 和 pushfq 之间,最后通过 jmp rax 进行跳转
对抗的思路就是把中间有效的指令提取出来,其他的 nop 掉,再计算出每个结构最后的跳转地址