简介 angr 是一个多架构的二进制分析工具包,能够对二进制文件执行动态符号执行(如 Mayhem、KLEE 等)和各种静态分析;angr 的核心特性包括控制流图(CFG)恢复、污点分析、符号执行、路径探索以及自动漏洞挖掘等,使用 Python 编写,接口灵活,适合快速搭建复杂的二进制分析工具
符号执行 输入: 符号变量X → 程序执行 → 收集所有可能的路径和约束条件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 'stdin_0' , 64 ) if input == "HelloAngr" :else :
安装 1 2 3 python3 -m venv angr_envsource angr_env/bin/activate
本文章的 angr 版本是 9.2.177
基本使用 参考 jakespringer/angr_ctf
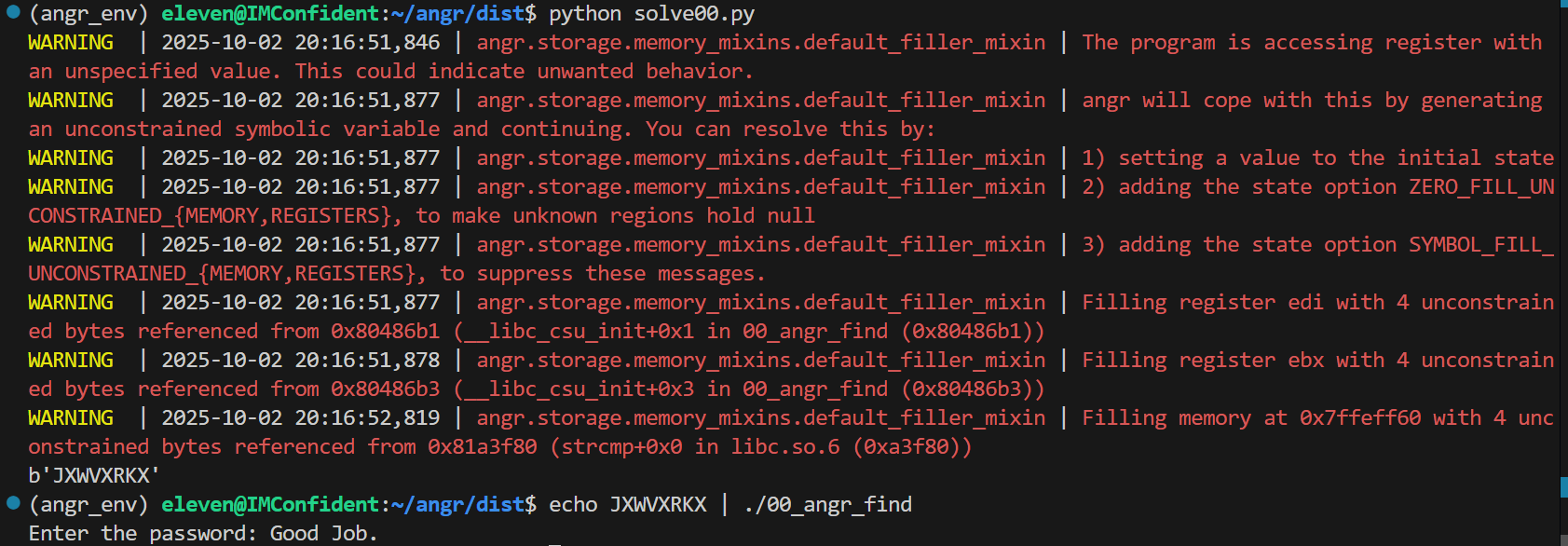
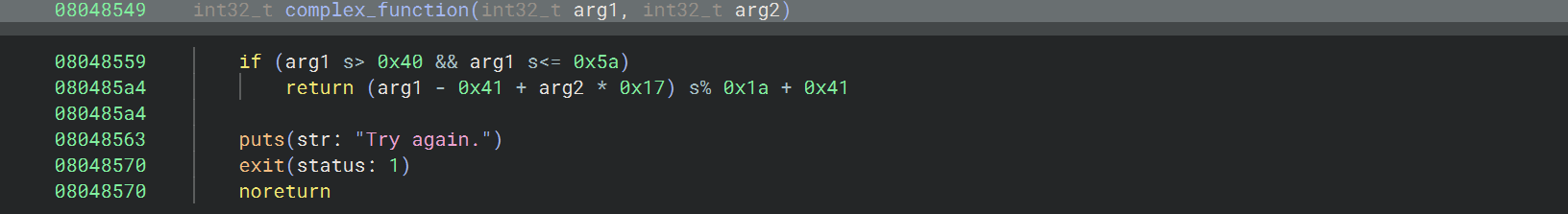
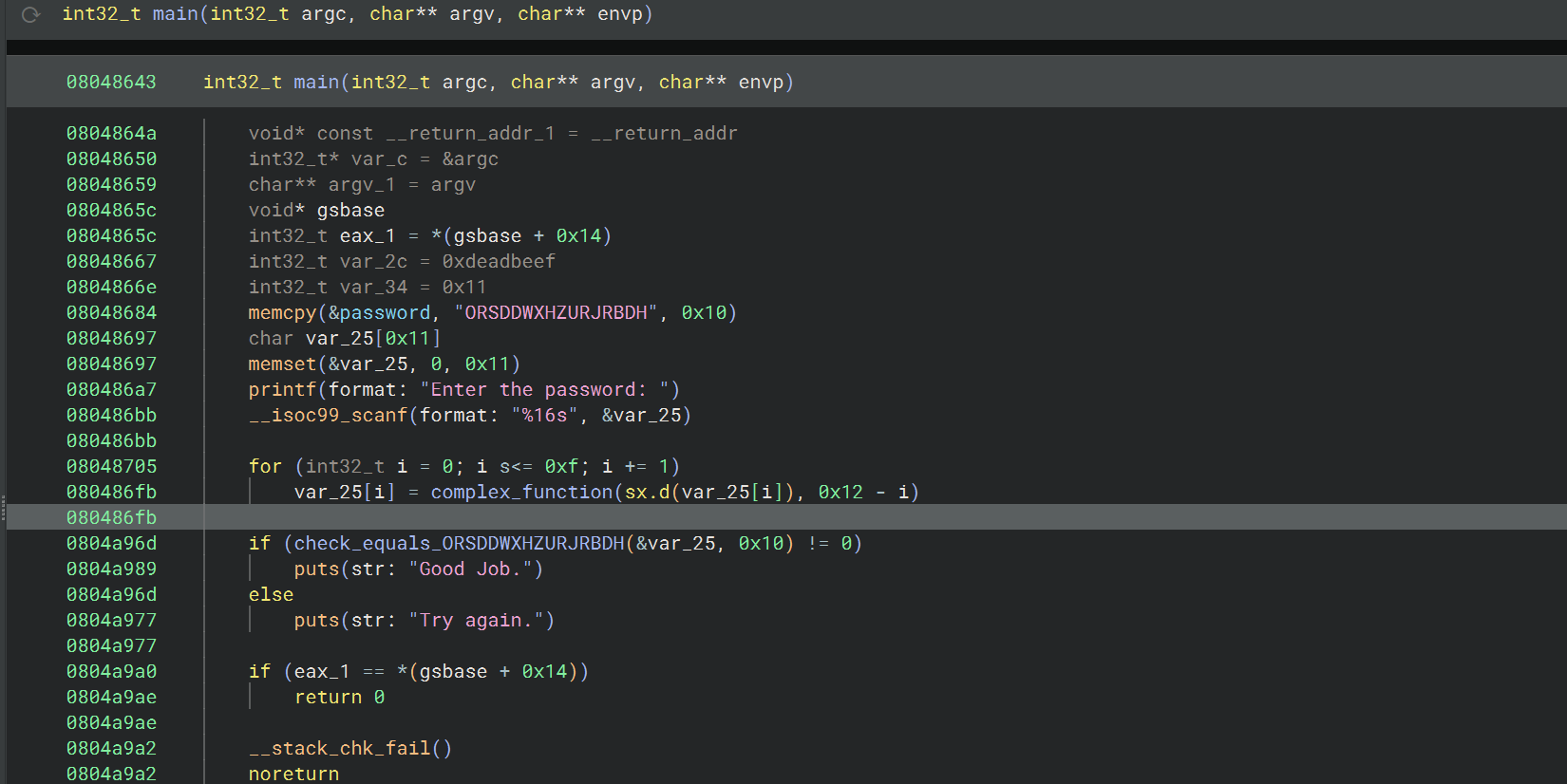
00_angr_find 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) int i; char s1[9 ]; unsigned int v6; 0x14u );printf ("Enter the password: " );"%8s" , s1);for ( i = 0 ; i <= 7 ; ++i )if ( !strcmp (s1, "JACEJGCS" ) )puts ("Good Job." );else puts ("Try again." );return 0 ;int __cdecl complex_function (int a1, int a2) if ( a1 <= 64 || a1 > 90 )puts ("Try again." );exit (1 );return (3 * a2 + a1 - 65 ) % 26 + 65 ;
关键汇编
1 2 3 4 5 .text: 08048675 loc_8048675: .text: 08048675 sub esp, 0 Ch.text: 08048678 push offset aGoodJob .text: 0804867 D call _puts.text: 08048682 add esp, 10 h
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./00_angr_find" 0x0804867D if simulation.found: 0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno())) else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
运行结果可以看到成功找到了解决方案并且得到正确输入
01_angr_avoid 用反编译器查看 main 函数时会反编译失败,提示 “The function is too large to analyze”
查看源码这道题应该是因为定义了一个巨大的宏字符串常量,宏展开导致 main 内嵌了超大字符串,编译后 main 变成超大函数
1 2 3 4 #define USERDEF "{{ userdef }}" #define LEN_USERDEF {{ len_userdef }} strncpy (password, USERDEF, LEN_USERDEF);
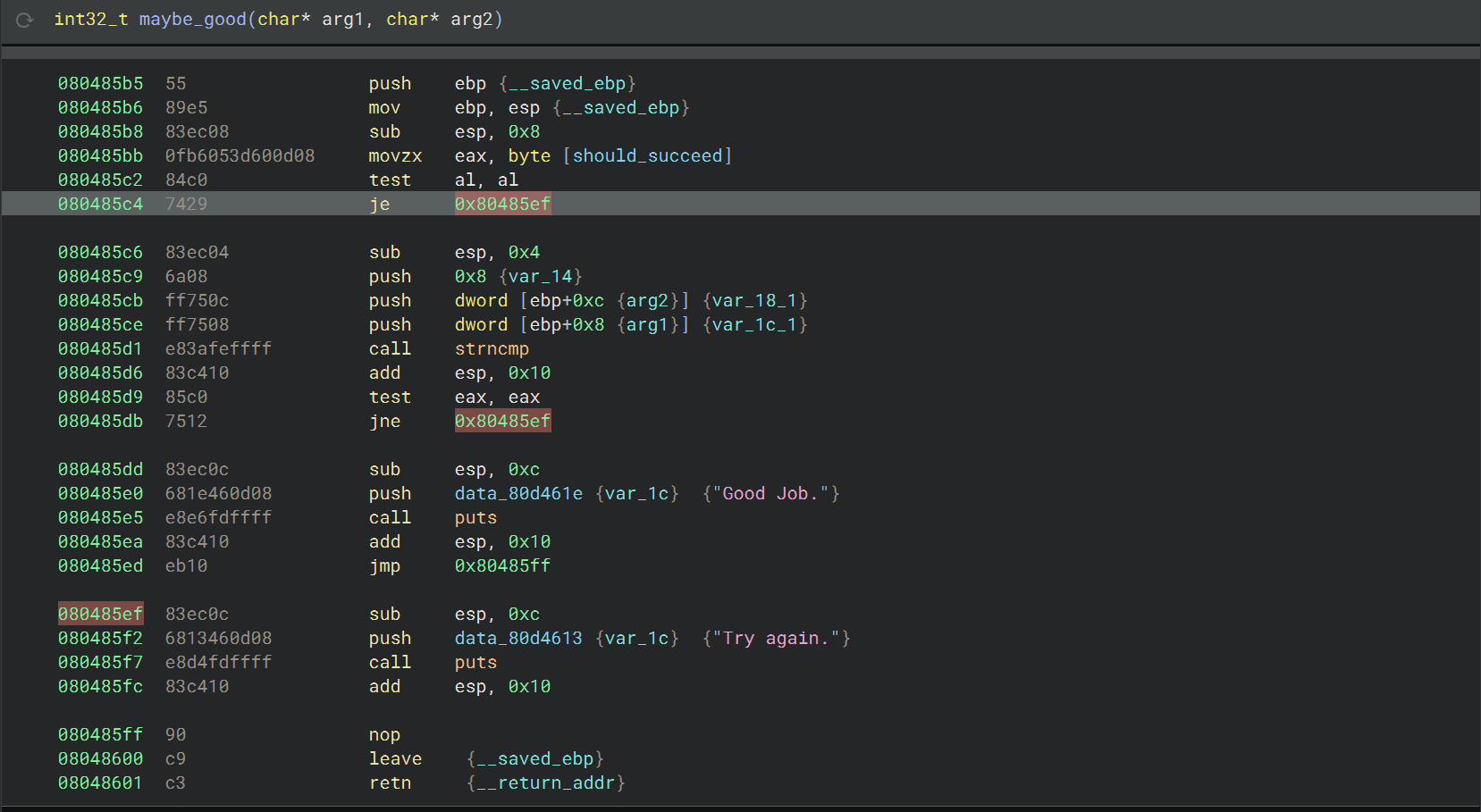
字符串搜索找到 “Good Job” 的地方
为了节省时间提高分析效率,在这里可以使用到 angr 中的 avoid 功能
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./01_angr_avoid" 0x080485e5 0x080485ef if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
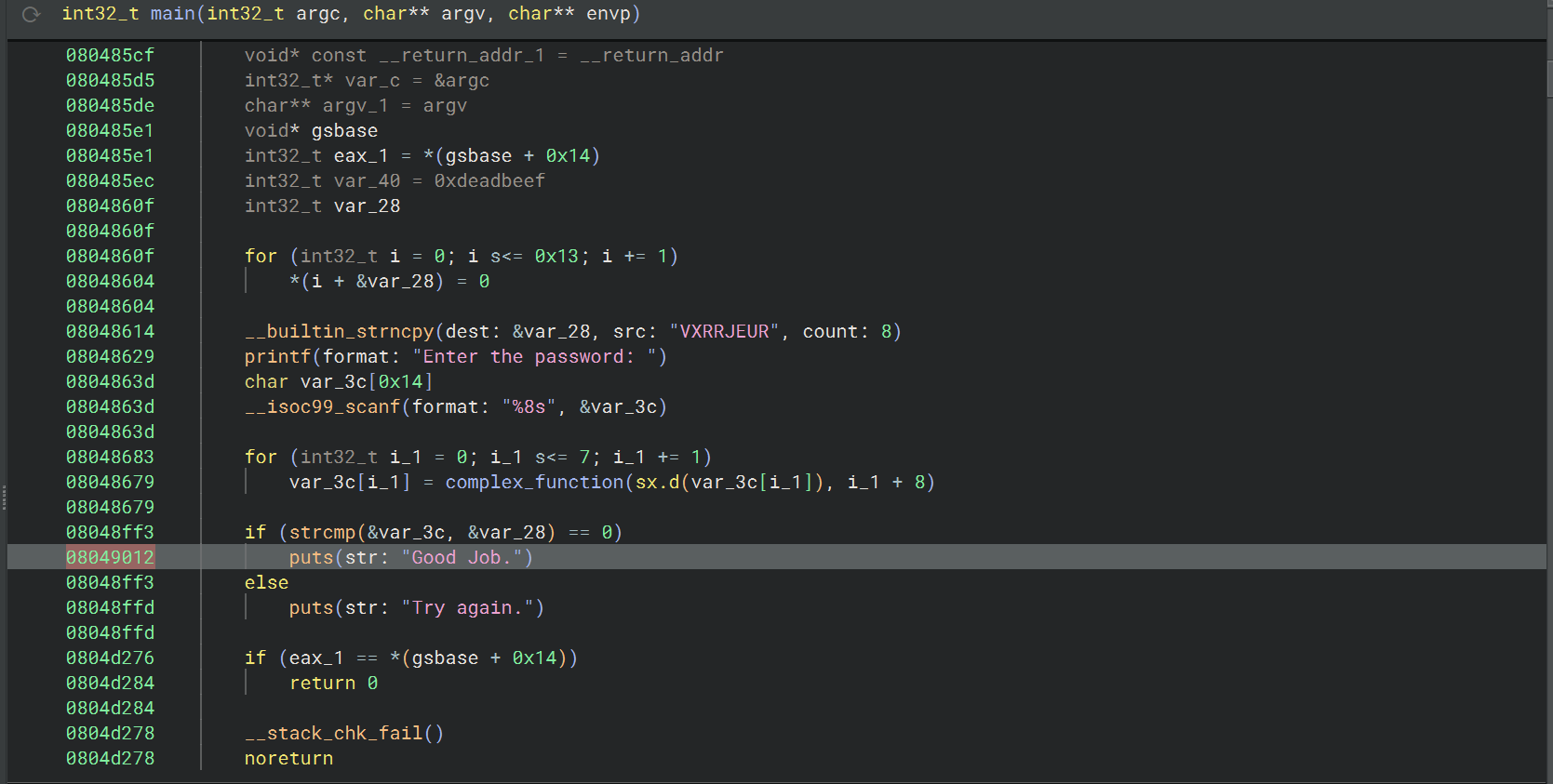
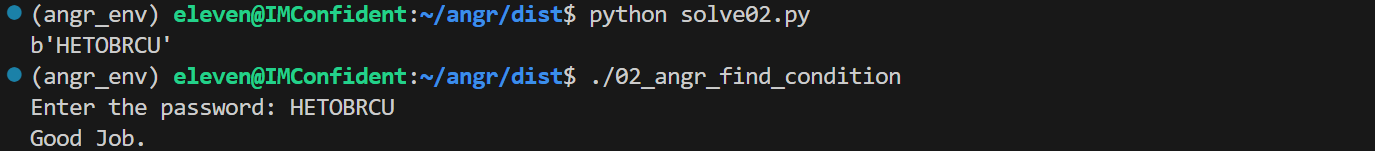
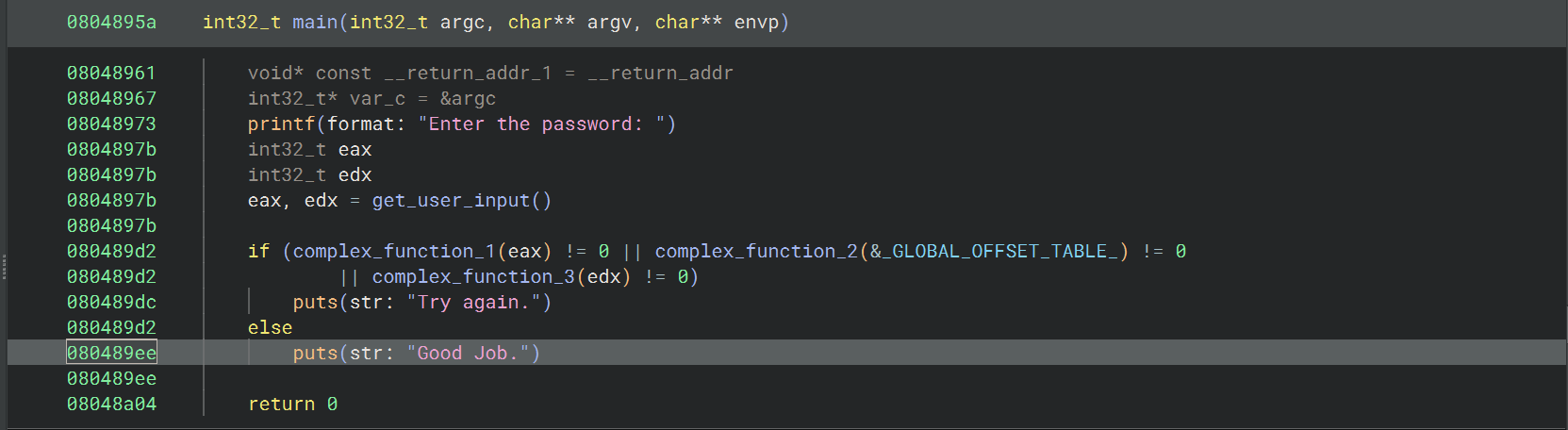
02_angr_find_condition 反编译看一下
先用 00 的方法试一下,find 的地址直接取了 main 函数中输出 “Good Job” 的地址 0x08049012
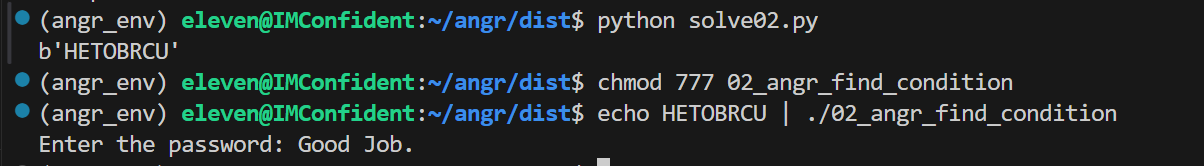
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./02_angr_find_condition" 0x08049012 if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
直接成功了
看看官方解答
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./02_angr_find_condition" def is_successful (state ):return b"Good Job." in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b"Try again." in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
依旧能得到正确结果
03_angr_symbolic_register
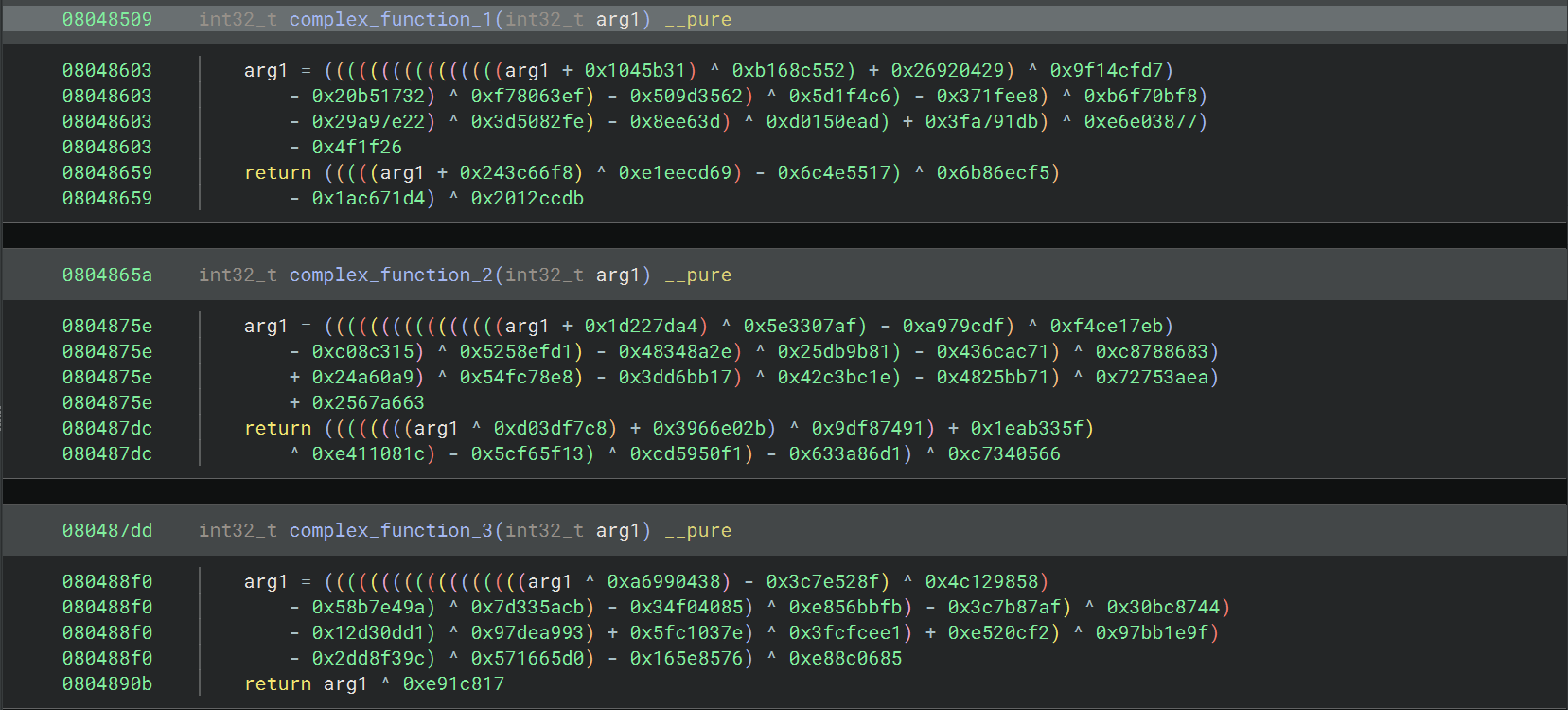
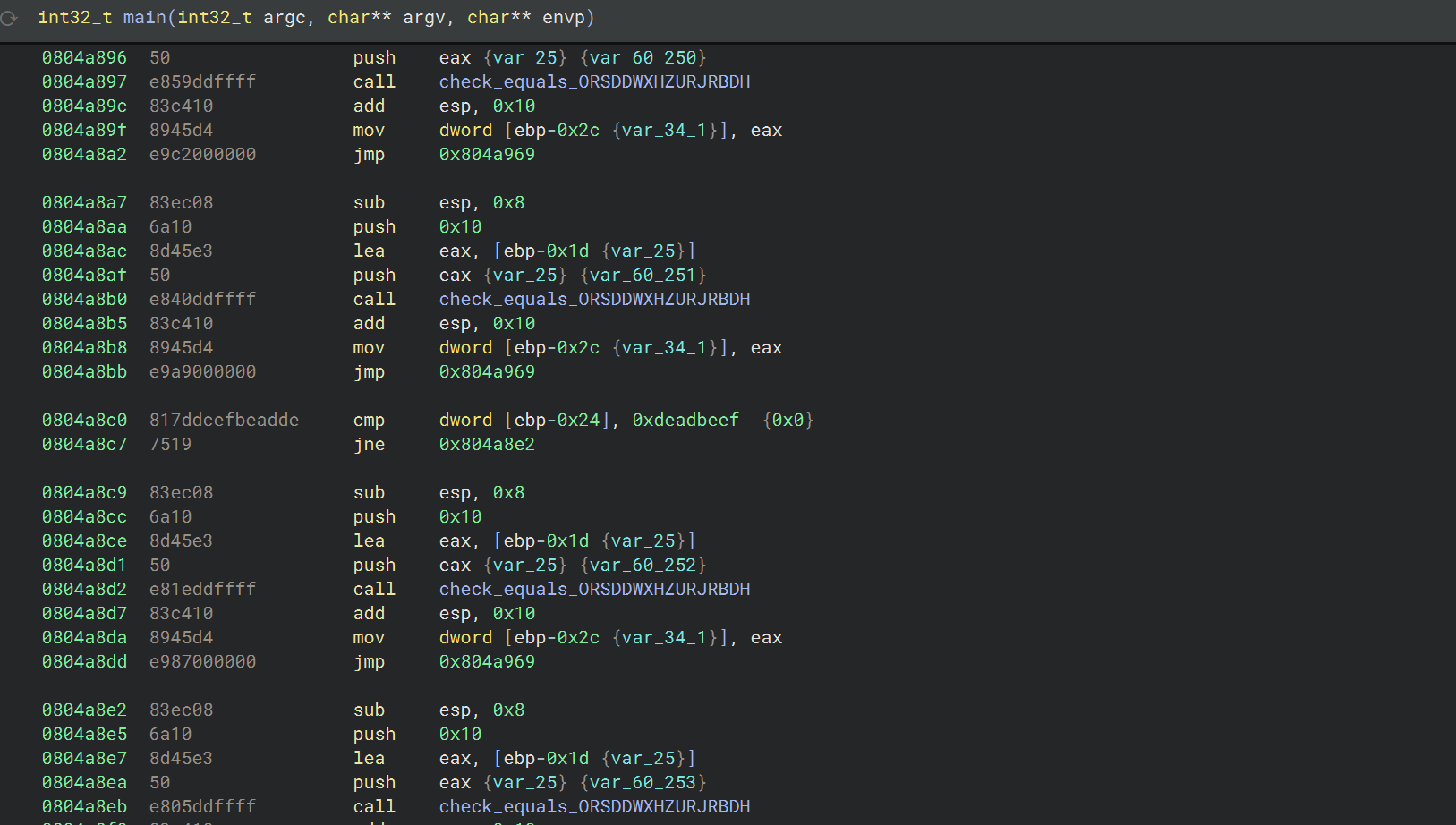
其中的三个 complex_function 就是很复杂的三个函数
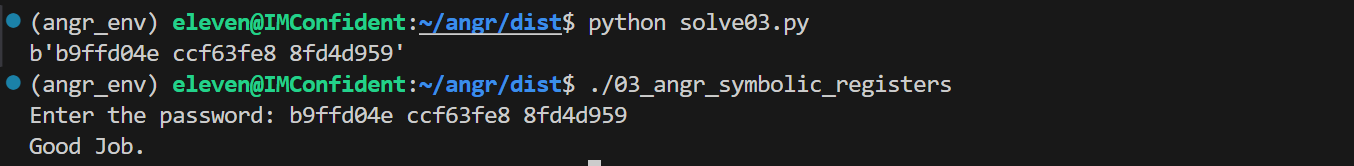
直接找输出 “Good Job” 的地址 0x080489ee
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./03_angr_symbolic_registers" 0x080489ee if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
可以得到正确结果
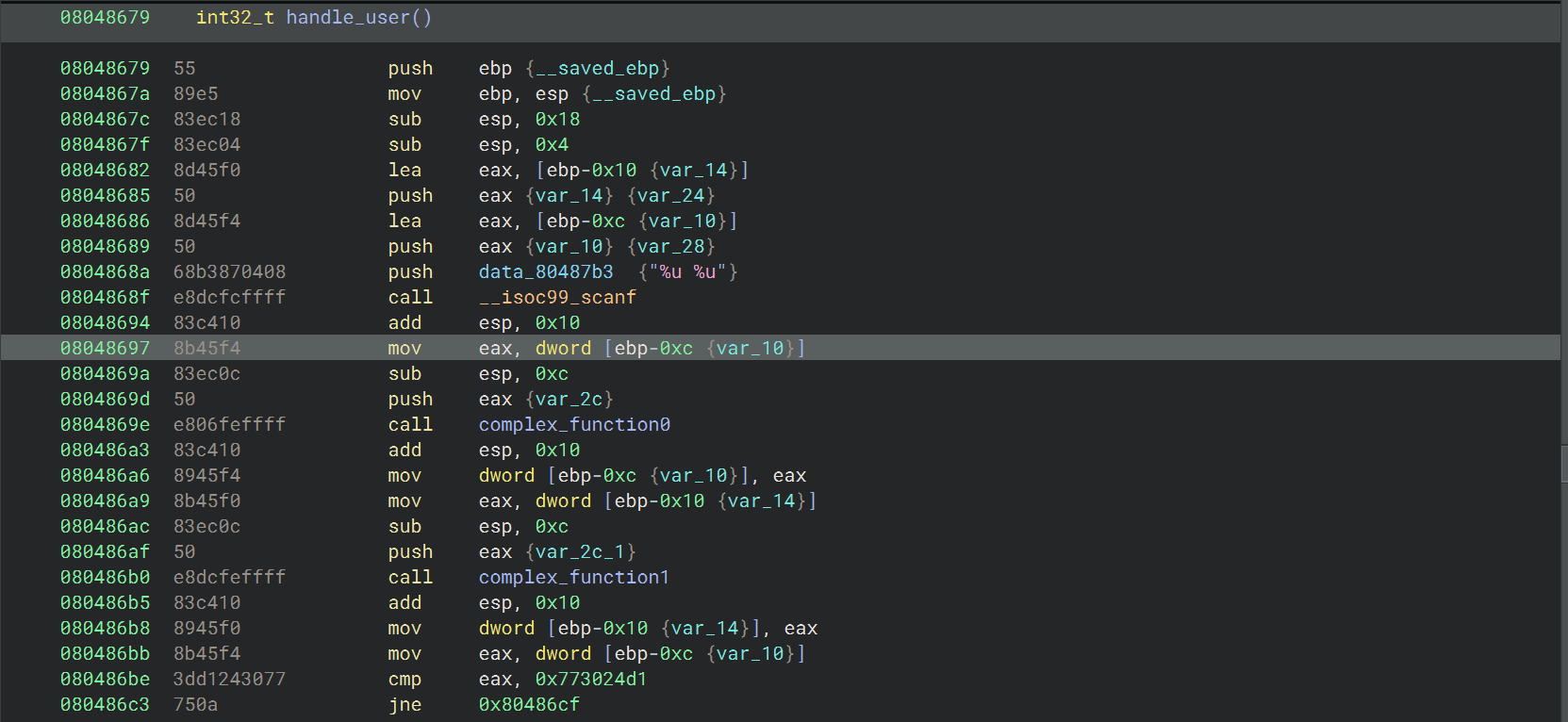
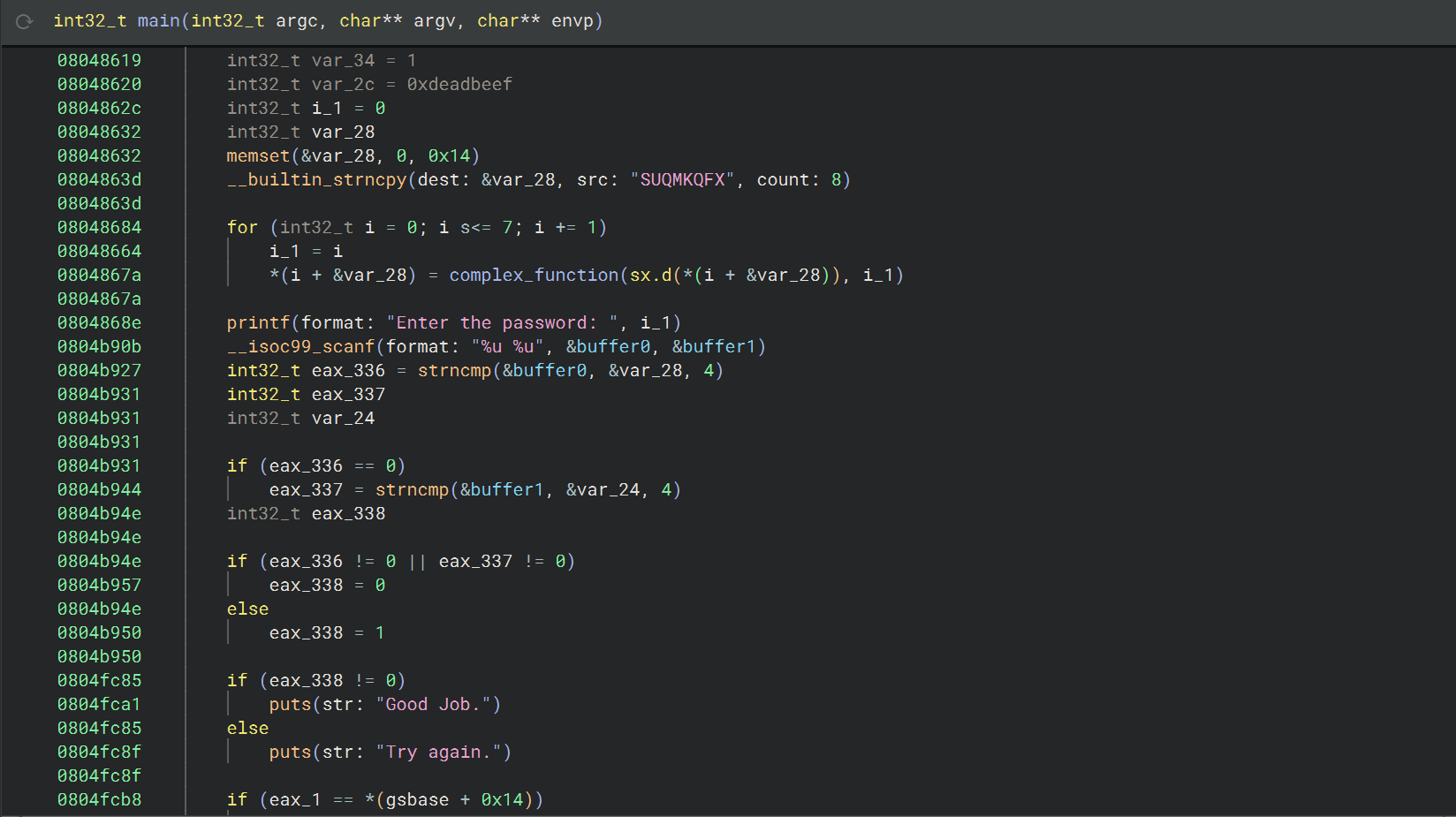
这道题的背景应该是针对旧版本的 Angr,当 scanf 读取多个输入时,例如 scanf(“%u %u”),Angr 内置的 scanf 不能直接模拟,需要手动创建符号变量并将其存储在正确的内存位置或寄存器中
大概是如下的模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 import angrimport claripy import sysdef main (argv ):"./03_angr_symbolic_registers" 0x08048937 32 'password0' , password0_size_in_bits)32 'password1' , password1_size_in_bits)32 'password2' , password2_size_in_bits)def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (password0)eval (password1)eval (password2)"{} {} {}" .format (solution0,solution1,solution2)print (solution)if __name__ == '__main__' :
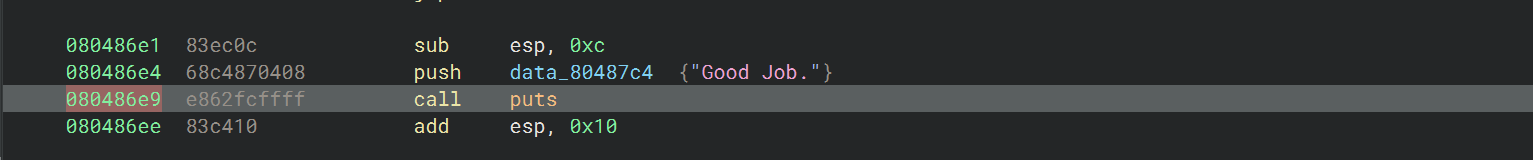
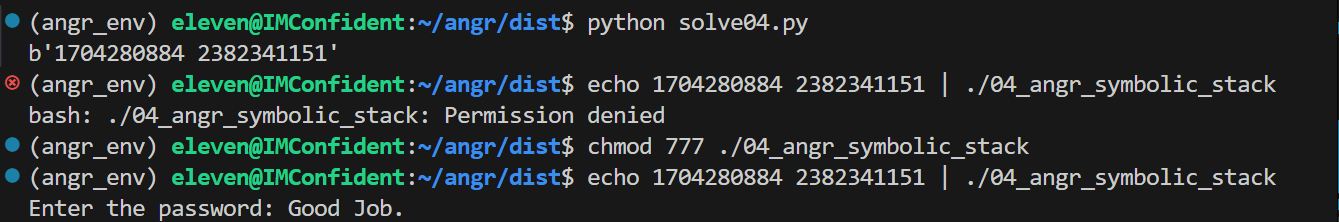
04_angr_symbolic_stack 搜索字符串定位输出到 “Good Job” 的地址 080486e9
和之前的脚本一样,只需要改个 path 和 print_good_address
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./04_angr_symbolic_stack" 0x080486E9 if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
得到正确输入
这道题是在学习符号化栈
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./04_angr_symbolic_stack" 0x08048697 0x18 'password0' , 32 )'password1' , 32 )0xc , password0, endness='Iend_LE' ) 0x10 , password1, endness='Iend_LE' )def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (password0)eval (password1)print (f"{solution0} {solution1} " )else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
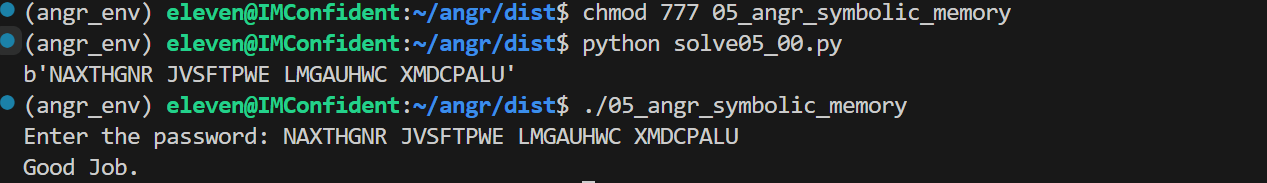
05_angr_symbolic_memory
直接用 print_good_address = 0x08048672 依旧可以得到正确输入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./05_angr_symbolic_memory" 0x08048672 if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
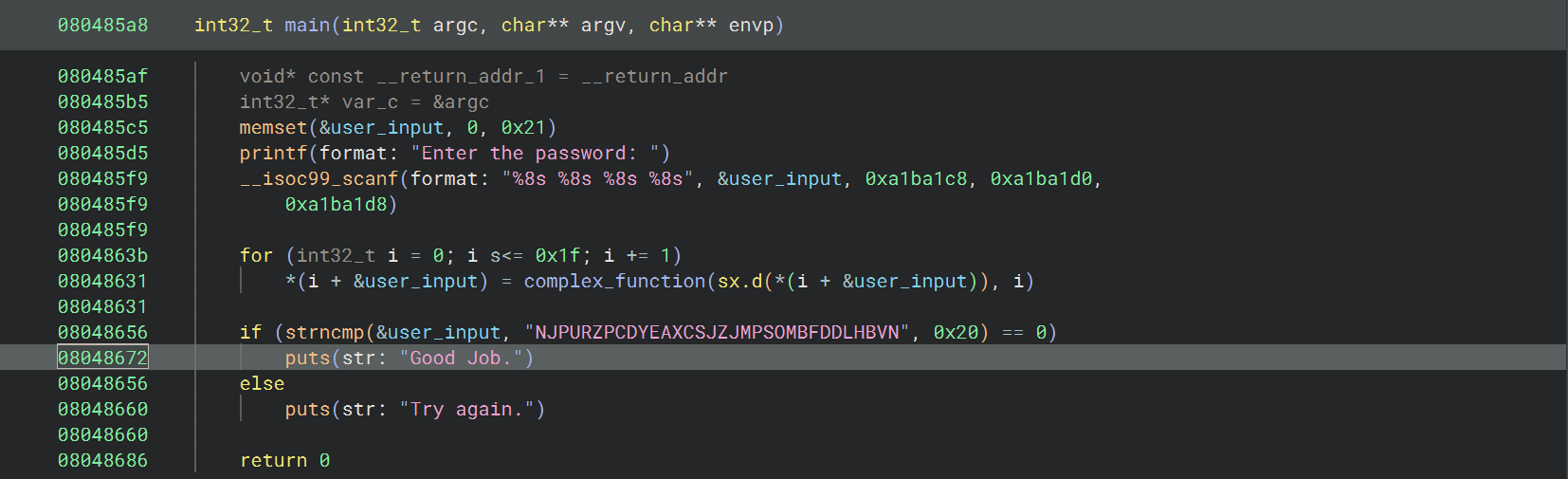
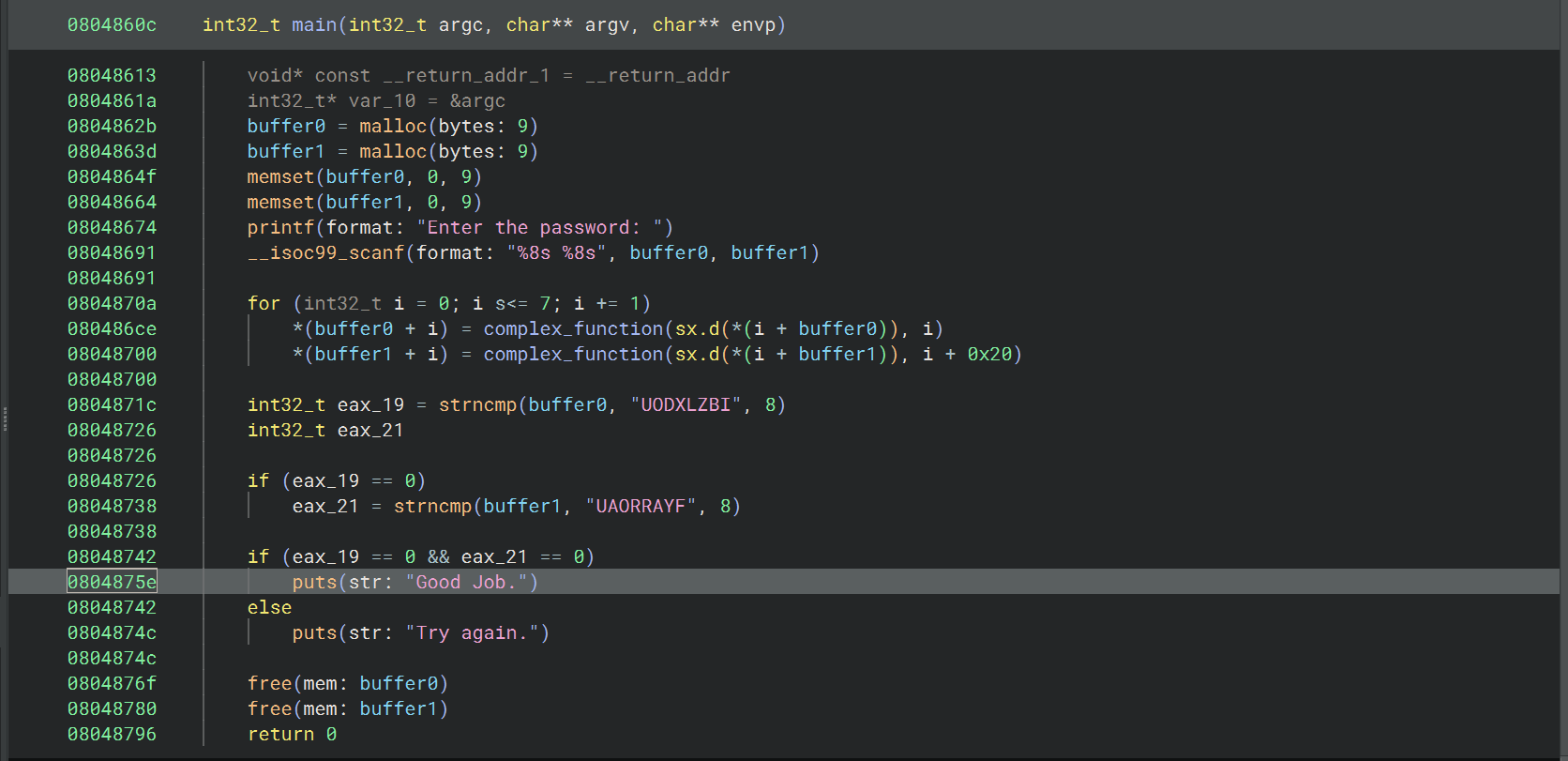
这道题是在学习符号化内存,本质上是在符号化 .bss 段(未初始化的全局变量)
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./05_angr_symbolic_memory" 0x08048601 'password0' , 64 )'password1' , 64 )'password2' , 64 )'password3' , 64 )0xa1ba1c0 0xa1ba1c8 0xa1ba1d0 0xa1ba1d8 def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (password0, cast_to=bytes ) eval (password1, cast_to=bytes )eval (password2, cast_to=bytes )eval (password3, cast_to=bytes )f"{solution0.rstrip(b'\\x00' ).decode()} {solution1.rstrip(b'\\x00' ).decode()} {solution2.rstrip(b'\\x00' ).decode()} {solution3.rstrip(b'\\x00' ).decode()} " print (solution)else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
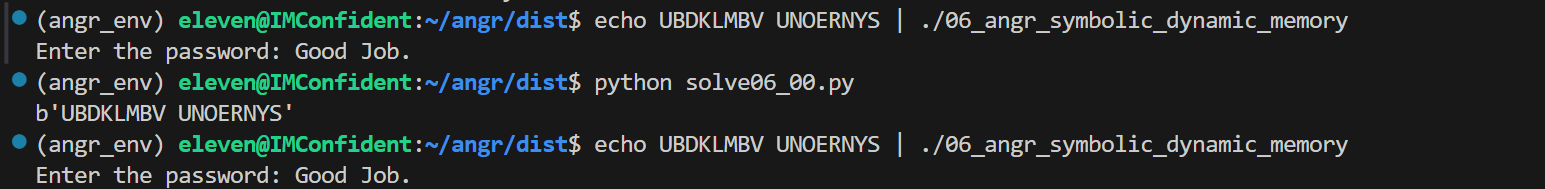
06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory
用 print_good_address = 0x0804875e 可以得到正确输入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory" 0x0804875e if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
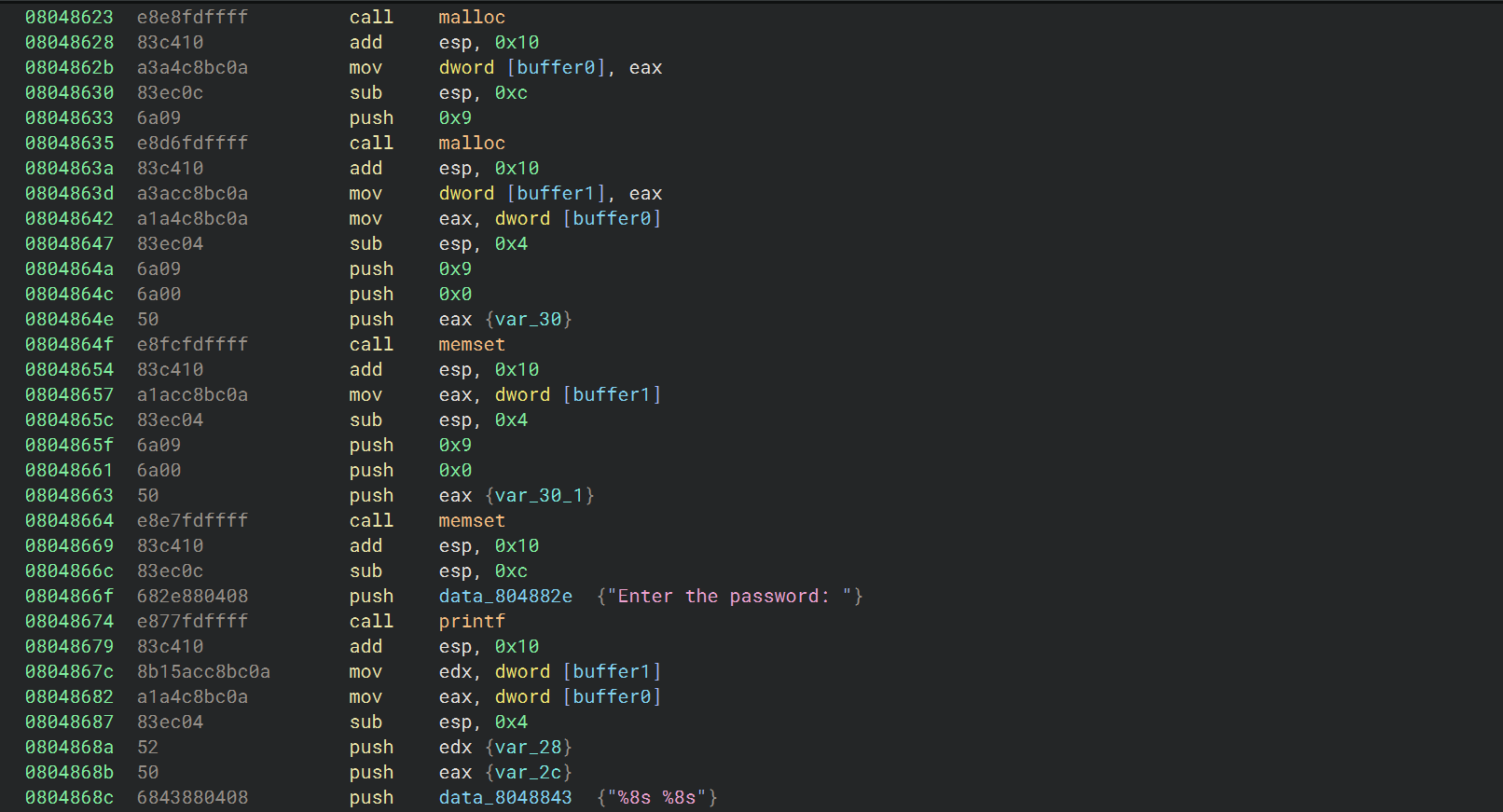
从汇编中可以看出,这道题的输入不是直接存储在栈上,而是通过 malloc 动态分配内存,然后将输入存储在这些动态分配的内存中
这就需要符号化动态内存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory" 0x08048699 'password0' , 64 )'password1' , 64 )0x10000000 0x10000010 0xabc8a4 0xabc8ac def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (password0, cast_to=bytes )eval (password1, cast_to=bytes )' ' + solution1.decode()print (solution)else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
从上面的几个例子也能看到有的地方新版的 angr 已经可以自动符号化,不需要手动创建符号化
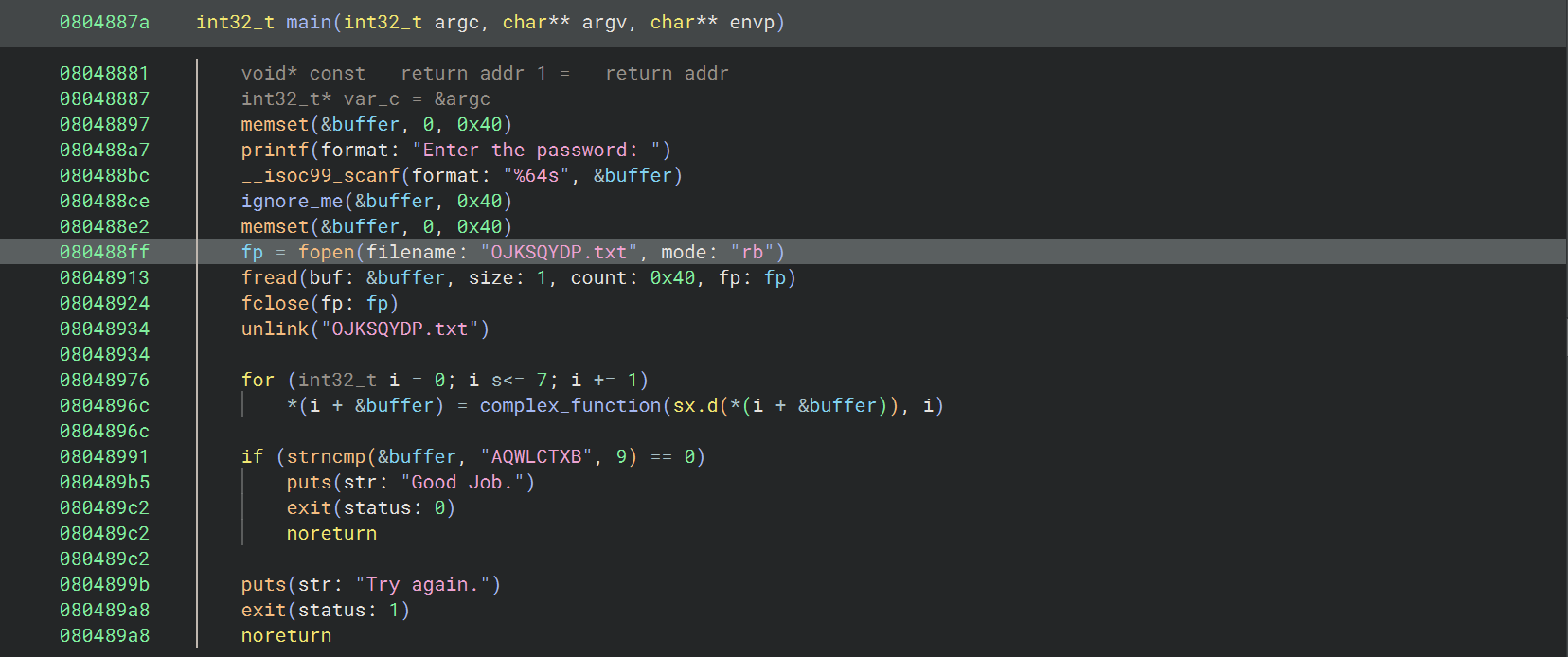
07_angr_symbolic_file 这个挑战和其他的不同,涉及到文件操作
其中 ignore_me 函数是将用户从控制台的输入写入一个文件(OJKSQYDP.txt),在 main 函数中通过 fread 从这个文件读取数据并进行验证
需要做的是:
确定程序中 fread 从哪个文件读取数据
使用 Angr 模拟文件系统,并用自定义的文件来替换真实文件
用符号变量初始化这个文件,使其被 fread 读取并传播到程序的执行状态中
使用 Angr 求解器来计算出正确的符号输入
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 import angr import claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./07_angr_symbolic_file" 0x080488d6 "OJKSQYDP.txt" 64 'password' , symbolic_file_size_bytes * 8 )def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (password, cast_to=bytes )'' .join(chr (b) if 32 <= b <= 126 else '.' for b in solution_bytes)print ("Solution (printable): {}" .format (printable_chars))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
运行结果
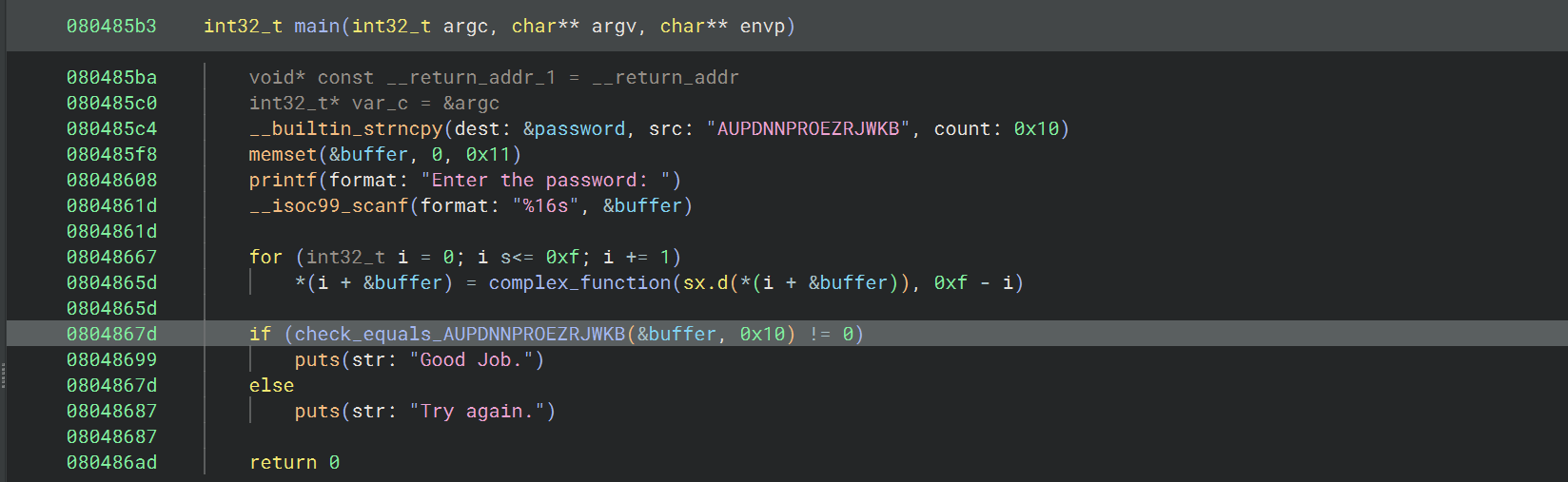
08_angr_constraints
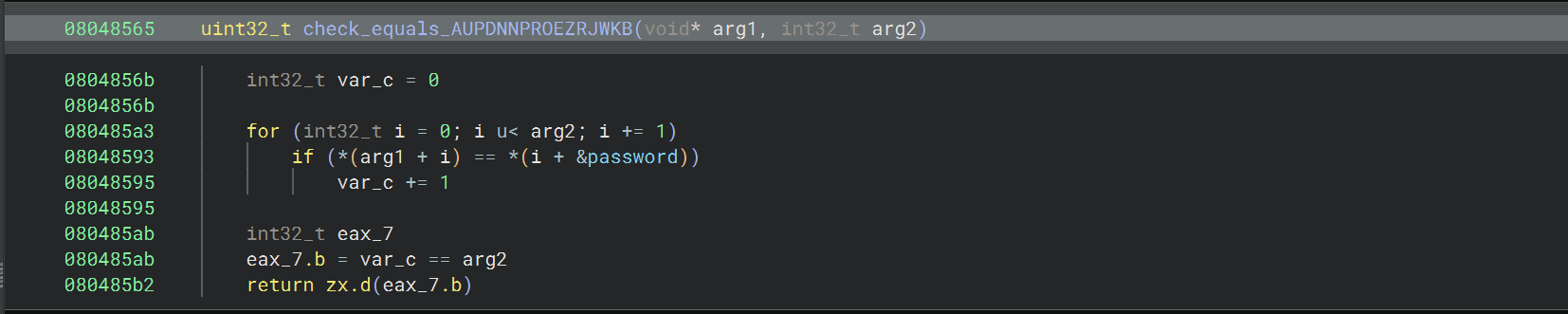
check 函数是这种模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int check_equals_AABBCCDDEEFFGGHH (char * to_check, size_t length) {uint32_t num_correct = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < length; ++i) {if (to_check[i] == REFERENCE_PASSWORD[i]) { 1 ;return num_correct == length;
这道题里面的比较函数是逐字符比较的,虽然和 strcmp(to_check, “AABBCCDDEEFFGGHH”) == 0 是同样的效果,但是用 angr 进行符号执行时,每一个要比较的字符 to_check[i] 都是一个未知的符号变量,所以这个 if 是一个分支点,每比较一种字符都有两种可能的路经(相等或不相等),这里长度是 16,总共有 2^16 = 65536 种可能的路径,这就产生了 angr 中的一个问题: 路径爆炸 ,路径爆炸会导致符号执行变得非常慢,甚至无法在合理时间内完成
要解决这个问题,可以使用 angr 的约束求解功能
在比较发生前停止,把被比较的数据直接约束为参考值,然后让 SMT 求解器反解出输入 password
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import angr import claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./08_angr_constraints" 0x08048625 'password' ,16 *8 )0x804a050 0x08048669 if simulation.found:0 ]0x804a050 16 b"AUPDNNPROEZRJWKB" eval (password, cast_to=bytes )print (solution.decode('utf-8' , errors='ignore' ))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
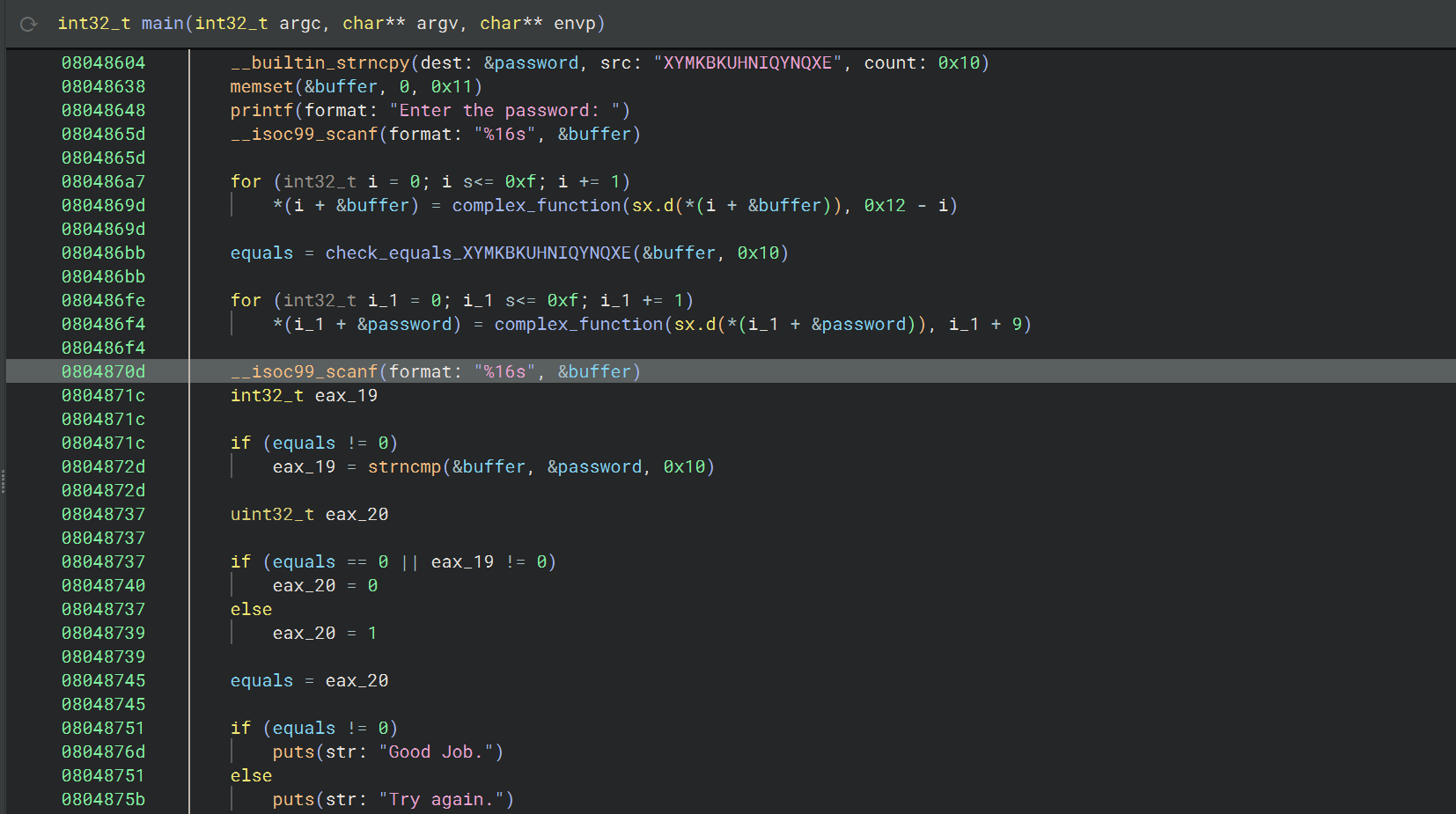
09_angr_hooks
程序读取了两次输入,第一次输入经过 complex_function 之后与目标字符串 password 比较,第二次输入与变换后的 password 比较
如果用符号执行解决的话,需要关注的依旧是检查函数 check_equals_XYMKBKUHNIQYNQXE,除了上文条件约束的方法,还可以使用 Angr 的 hook 功能@project.hook(addr, length=n)
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./09_angr_hooks" 0x080486b3 5 @project.hook(check_equals_called_address, length=instruction_to_skip_length ) def skip_check_equals_ (state ):0x804a054 16 b"XYMKBKUHNIQYNQXE" 1 , 32 ), 0 , 32 )def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]print (solution)else :raise Exception("Could not find a solution" )if __name__ == "__main__" :
10_angr_simprocedures
这个挑战与之前的相似,也是要处理 check 函数,但是通过汇编可以看到,check_equals_ 被调用的次数太多了,如果在每个调用点单独进行 hook,那就不太实际了;而且这道题的输入也是存储在动态的栈地址,
可以使用 SimProcedure 来编写自己的 check_equals_ 实现,然后 hook check_equals_ 这个符号,从而一次性替换所有对 check_equals_ 的调用
定义一个继承自 angr.SimProcedure 的类,以便利用 Angr 的 SimProcedure 功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 int add_if_positive (int a, int b) {if (a > 0 && b > 0 ) {return a + b;else {return 0 ;
这个函数可以用下面的方式进行模拟:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class ReplacementAddIfPositive (angr.SimProcedure):def run (self, a, b ):if a >= 0 and b >=0 :return a + belse :return 0
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./10_angr_simprocedures" class ReplacementCheckEquals (angr.SimProcedure):def run (self, to_check, length ):self .state.memory.load(b"ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH" return claripy.If(1 , 32 ), 0 , 32 )"check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH" def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]print (solution)else :raise Exception("Could not find a solution" )if __name__ == "__main__" :
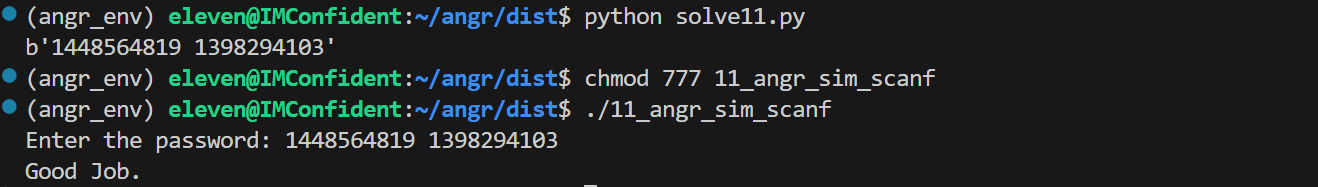
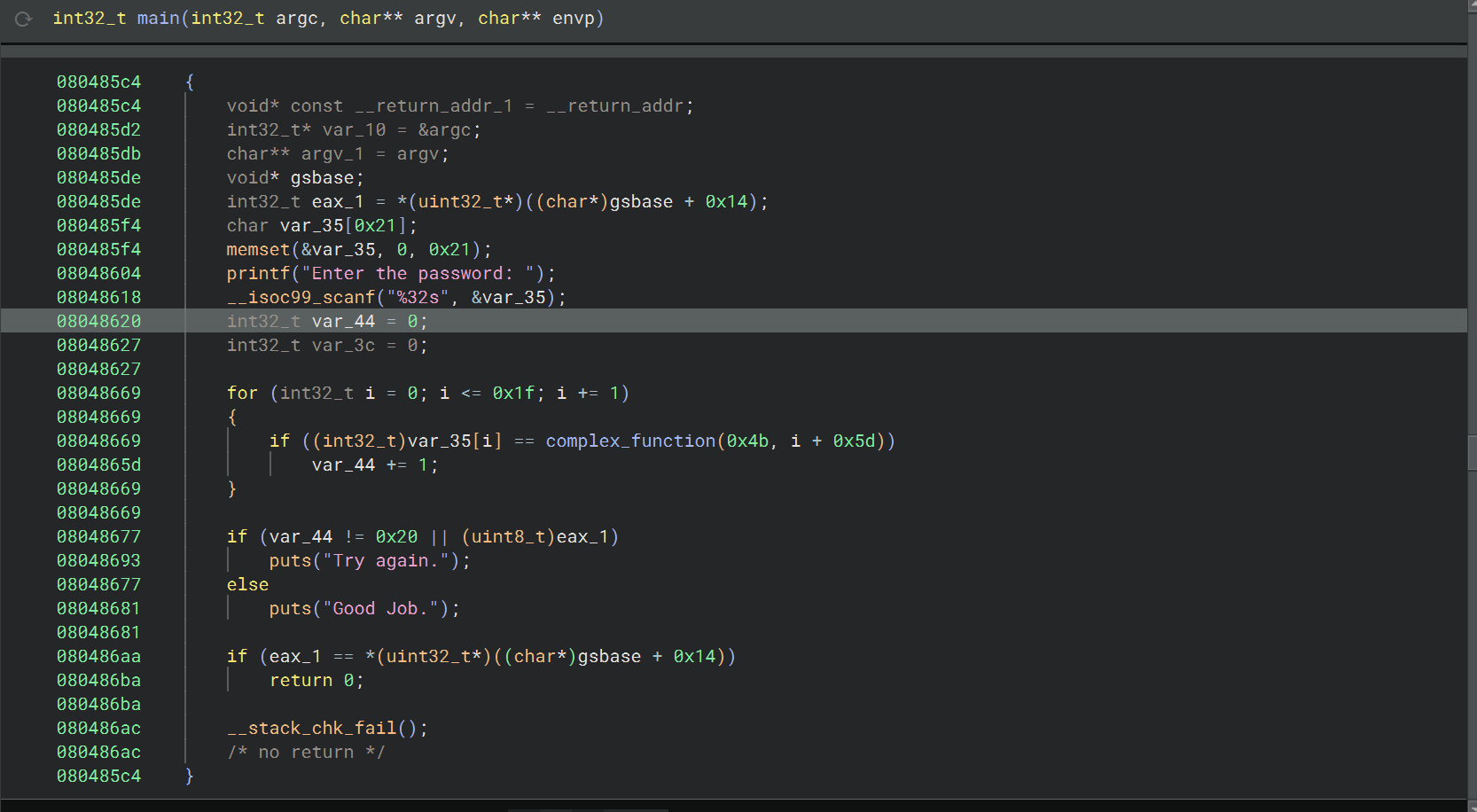
11_angr_sim_scanf
这道题的背景是旧版的 Angr 不支持 scanf 读取多个输入,所以 hook 掉 scanf,替换成自己实现的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./11_angr_sim_scanf" def is_successful (state ):return b"Good Job." in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b"Try again." in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
贴一下 hook scanf 的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import angrimport claripyimport sysdef main (argv ):"./11_angr_sim_scanf" class ReplacementScanf (angr.SimProcedure):def run (self, format_string, scanf0_address, scanf1_address ):'scanf0' , 32 )'scanf1' , 32 )self .state.memory.store(scanf0_address, scanf0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)self .state.memory.store(scanf1_address, scanf1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)self .state.globals ['solution0' ] = scanf0self .state.globals ['solution1' ] = scanf1return 2 '__isoc99_scanf' , ReplacementScanf())def is_successful (state ):return b'Good Job.' in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b'Try again.' in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]eval (solution_state.globals ['solution0' ])eval (solution_state.globals ['solution1' ])print (f"{solution0} {solution1} " )else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
12_angr_veritesting
与之前的不同,这道题是对每个输入字符单独混淆并且每次字符立即比较,产生了大量的分支
使用 Angr 中的一个优化技术 Veritesting 减少符号执行的路径爆炸问题simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state, veritesting=True)
Veritesting 结合了静态分析和动态分析,当遇到可能导致路径爆炸的代码块时,它暂停盲目的路径分叉,将接下来的一片代码区域当作一个整体进行静态分析和合并,生成统一的路径约束,用条件表达式(如 if-then-else)表示不同路径的结果,从而避免每遇到分支就分裂状态
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./12_angr_veritesting" True )def is_successful (state ):return b"Good Job." in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b"Try again." in stdout_outputif simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()))else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
13_angr_static_binary 对于静态链接的二进制文件,需要手动 hook 这些库函数,把它们替换成 Angr 内置的 SimProcedure,这样就可以跳过库函数内部复杂的执行https://github.com/angr/angr/tree/master/angr/procedures/libc
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘fopen’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘fclose’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘fwrite’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘getchar’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘strncmp’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘strcmp’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘scanf’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘printf’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘puts’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘libc’][‘exit’]
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES[‘glibc’][‘__libc_start_main’]
Angr 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 import angrimport sysdef main (argv ):"./13_angr_static_binary" 0x0804ed40 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['printf' ]())0x0804ed80 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['scanf' ]())0x0804f350 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['puts' ]())0x08048d10 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['glibc' ]['__libc_start_main' ]())def is_successful (state ):return b"Good Job." in stdout_outputdef should_abort (state ):return b"Try again." in stdout_output if simulation.found:0 ]print (solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()).decode())else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
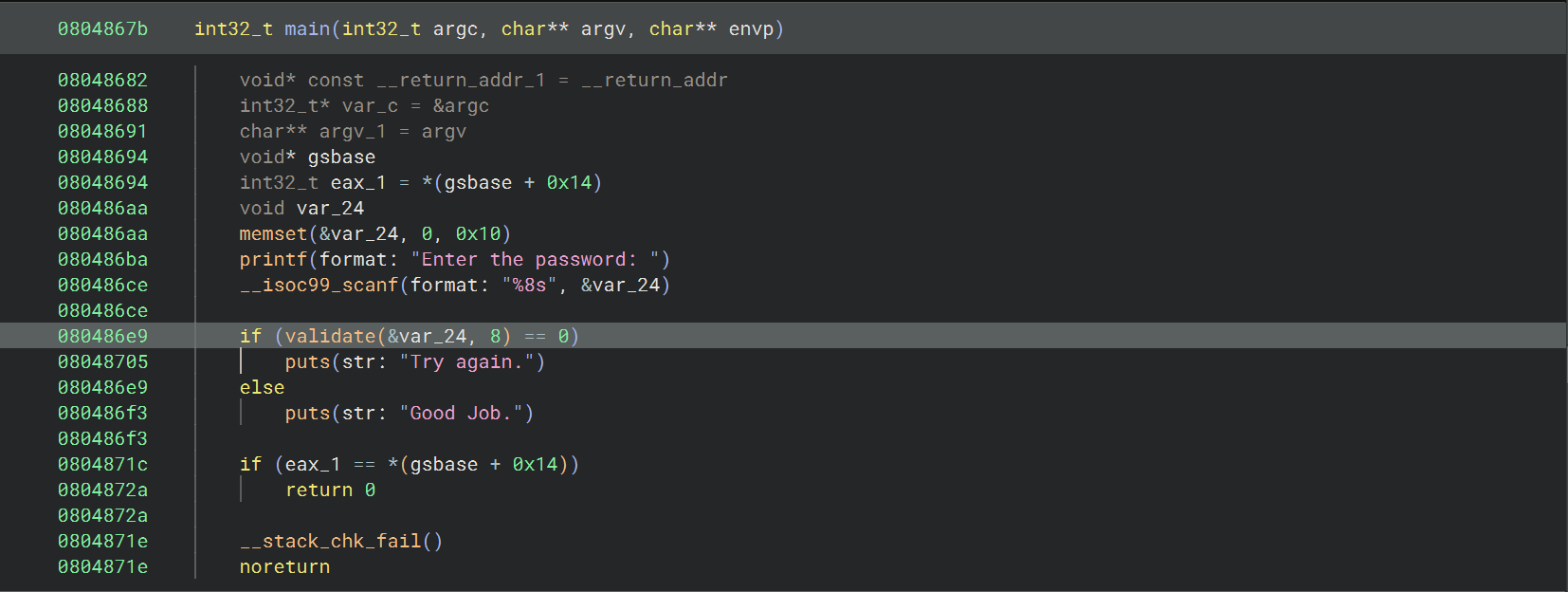
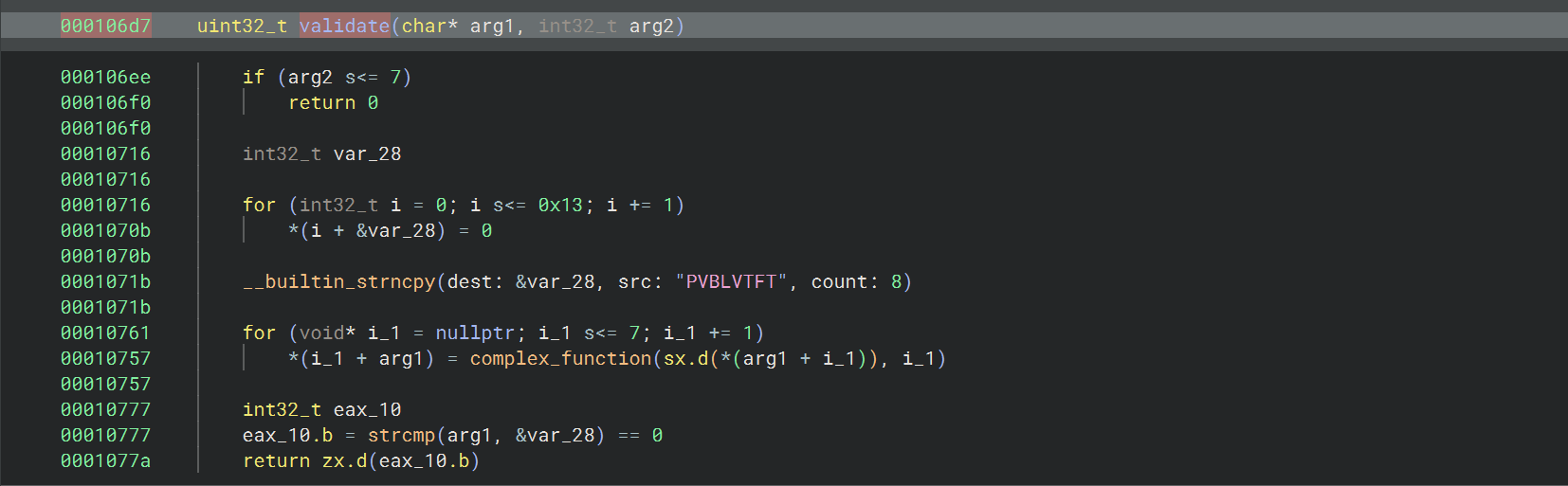
14_angr_shared_library 这道题给了一个共享链接库文件,程序中的 validate 函数就是从这个库文件中导入的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 000106d7 uint32_t validate(char* arg1, int32_t arg2)000106d7 55 push ebp {__saved_ebp}000106d8 89e5 mov ebp, esp {__saved_ebp}000106 da 56 push esi {__saved_esi}000106 db 53 push ebx {__saved_ebx} {_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_}000106 dc 83 ec20 sub esp, 0 x20000106 df e81cfeffff call __x86.get_pc_thunk.bx000106e4 81 c31c190000 add ebx, 0 x191c {_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_}000106 ea 837d0 c07 cmp dword [ebp+0 xc {arg2}], 0 x7000106 ee 7 f0a jg 0 x106fa000106 f0 b800000000 mov eax, 0 x0000106 f5 e983000000 jmp 0 x1077d000106 fa c745f400000000 mov dword [ebp-0 xc {i}], 0 x000010701 eb0f jmp 0 x1071200010703 8d55 dc lea edx, [ebp-0 x24 {var_28}]00010706 8 b45f4 mov eax, dword [ebp-0 xc {i}]00010709 01d0 add eax, edx {var_28}0001070 b c60000 mov byte [eax], 0 x00001070 e 8345 f401 add dword [ebp-0 xc {i}], 0 x100010712 837 df413 cmp dword [ebp-0 xc {i}], 0 x1300010716 7 eeb jle 0 x1070300010718 8d45 dc lea eax, [ebp-0 x24 {var_28}]0001071 b c7005056424c mov dword [eax {var_28}], 0 x4c42565000010721 c7400456544654 mov dword [eax+0 x4 {var_24}], 0 x5446545600010728 c745f000000000 mov dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}], 0 x00001072 f eb2c jmp 0 x1075d00010731 8 b55f0 mov edx, dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}]00010734 8 b4508 mov eax, dword [ebp+0 x8 {arg1}]00010737 8d3402 lea esi, [edx+eax]0001073 a 8 b55f0 mov edx, dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}]0001073 d 8 b4508 mov eax, dword [ebp+0 x8 {arg1}]00010740 01d0 add eax, edx00010742 0 fb600 movzx eax, byte [eax]00010745 0 fbec0 movsx eax, al00010748 83 ec08 sub esp, 0 x80001074 b ff75f0 push dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}] {var_38_1}0001074 e 50 push eax {var_3c_1}0001074 f e86cfdffff call complex_function00010754 83 c410 add esp, 0 x1000010757 8806 mov byte [esi], al00010759 8345 f001 add dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}], 0 x10001075 d 837 df007 cmp dword [ebp-0 x10 {i_1}], 0 x700010761 7 ece jle 0 x1073100010763 83 ec08 sub esp, 0 x800010766 8d45 dc lea eax, [ebp-0 x24 {var_28}]00010769 50 push eax {var_28} {var_38_2}0001076 a ff7508 push dword [ebp+0 x8 {arg1}] {var_3c_2}0001076 d e82efdffff call strcmp00010772 83 c410 add esp, 0 x1000010775 85 c0 test eax, eax00010777 0 f94c0 sete al0001077 a 0 fb6c0 movzx eax, al0001077 d 8d65 f8 lea esp, [ebp-0 x8]00010780 5 b pop ebx {__saved_ebx}00010781 5 e pop esi {__saved_esi}00010782 5 d pop ebp {__saved_ebp}00010783 c3 retn {__return_addr}
Angr 代码:
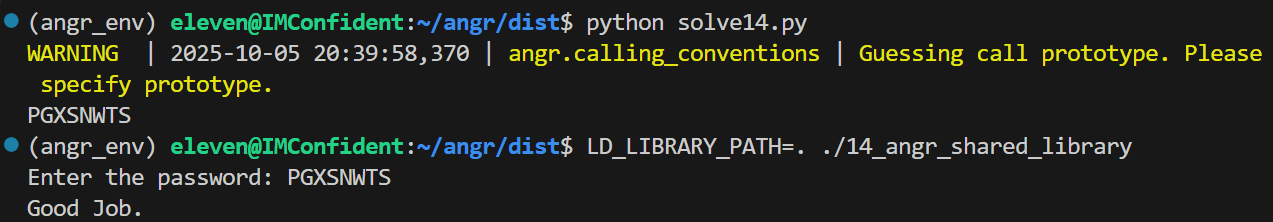
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import angrimport claripyimport sys def main (argv ):"./lib14_angr_shared_library.so" 0x10000 'main_opts' : { 'base_addr' : base 0x3000000 , 32 ) 0x6d7 8 , 32 ),'password' , 8 *8 ) 0x77d if simulation.found:0 ]0 )eval (password,cast_to=bytes ).decode()print (solution)else :raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )if __name__ == '__main__' :
参考文章:https://github.com/jakespringer/angr_ctf/tree/master/solutions https://3cly.github.io/2023/04/16/Angr%E7%AC%A6%E5%8F%B7%E6%89%A7%E8%A1%8C%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0/ https://www.kn0sky.com/?p=0e2f9462-df20-4705-83c2-4ff36b5b0c40#angr-%E5%88%9D%E5%AD%A6%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0