Angr 反混淆对抗 OLLVM
参考是 https://bbs.kanxue.com/thread-286549.htm
以下都是对这位师傅文章的学习,做个记录
对抗控制流平坦化 FLA
Control Flow Flattening
其主要目标是打乱程序原有的控制流结构(如 if/else、for、while、switch 等),干扰静态分析
原始代码
1 | |
对应流程图
1 | |
控制流平坦化的核心思想:
把原本的结构化控制流打散成多个基本块;用分发器和状态变量来控制基本块的执行顺序;去掉原有的直接跳转关系(比如 if/else 分支),改为通过修改状态变量 + switch/case 来控制跳转使
平坦化之后的代码
1 | |
对应流程图
1 | |
实际遇到的控制流平坦化远比示例复杂
一般标准的控制流平坦化 CFG 如下
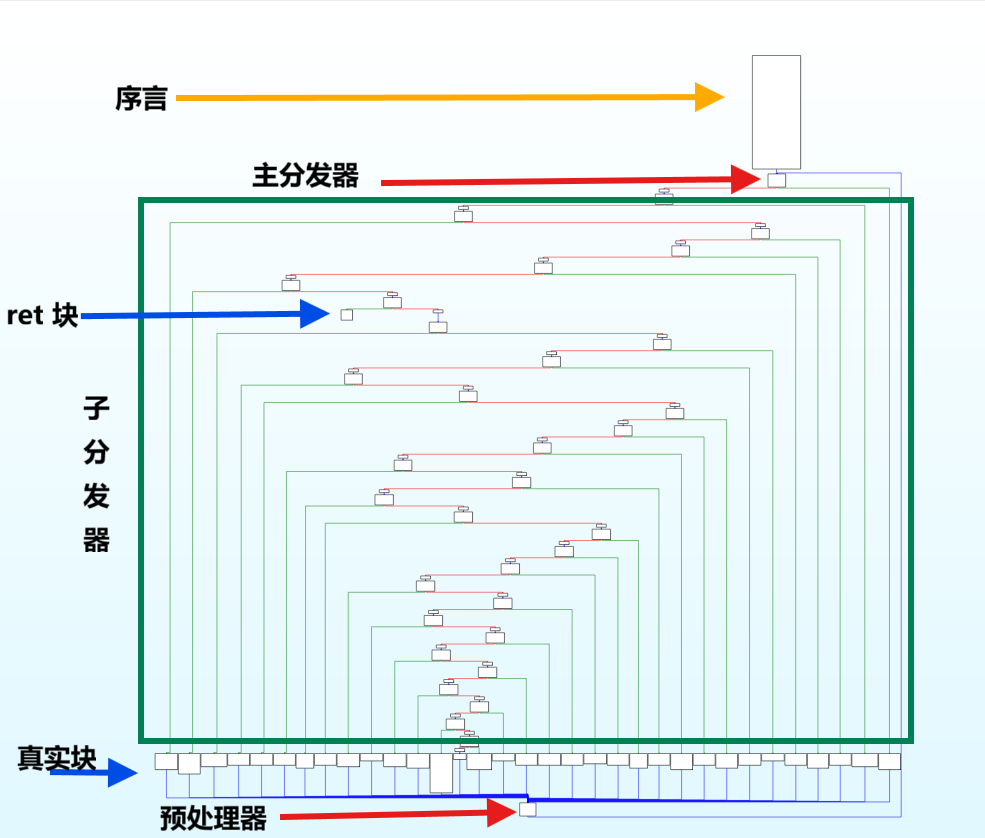
序言:函数开始执行的第一个基本块
主/子分发器:控制基本块执行顺序,序言的后继为主分发器
预处理器:其后继为主分发器
ret 块:函数出口,它是没有后继的
真实块:混淆前的基本块,包含实际的代码逻辑,其后继为预处理器
ps:有关前驱和后继
1 | |
处理思路:
- 找到所有真实块
- 找到真实块之间原本的跳转关系
- 重建控制流
找到所有真实块
- 找到主分发器(循环头)
- 找到预处理器(汇聚块)
- 找到 ret 块
- 找到混淆前的真实块
找循环头
使用 BFS 遍历 CFG,记录从起始块到每个块的路径,一旦在路径中发现某个块再次出现,说明有回路,这个块的起始地址就是一个循环头
1 | |
当后继再次遇到 C,就说明 D → C 是一条回路,因此 C 是一个循环头
1 | |
找汇聚块
对于标准的 FLA,循环头有两个前驱,一个是序言块,一个是汇聚块
示例的这个非标准的 FLA,其循环头和汇聚块的地址是相同的
1 | |
找真实块
找到汇聚块之后就可以通过寻找其前驱的方式找到混淆前的所有真实块了
对于非标准的 FLA,汇聚块的前驱包含了序言块
而对于标准的 FLA,获取序言块需要从循环头的前驱中寻找并剔除掉其中的汇聚块
除此之外,还要注意的一个点是,有的基本块的尾部指令是相同的,反编译器在处理时会把它拿出来共享,这种情况下就需要把这些块的前驱也考虑进去,否则找到的真实块会不完整
示例:函数 sub_41D08 (sub441D08)中的 0x42288(0x00442288) 处
1 | |
找 ret 块
对于标准的 FLA,一般直接找没有后继的块即可
但是对于非标准的 FLA,只关注没有后继的块会遗漏部分真实代码 (0x42AB0处)
除此之外,还要考虑单跳转块和子分发器的情况
1 | |
这样使得最后返回的 block :
如果有单跳转->回溯到上一个真实块
如果有子分发器->回退到 ori_ret_block
否则就是一开始找到的 ret 块
1 | |
输出:
1 | |
找到真实块之间的关系
由上述步骤我们已经找到了所有的真实块,接下来要做的就是找到这些真实块之间的跳转关系
这里就使用到了 Angr 来处理,为了避免一次性执行完整个程序发生路径爆炸,导致执行失败的问题,我们采用分块单独执行的方式,每次执行只取 real_blocks 中的一个块,如第一次取 real_blocks[0] 开始执行,当执行到的地址在保存的真实块地址列表中时,就停止执行,保存当前状态,记录下这个块连接关系;然后取下一个真实块 real_blocks[1] 作为新的初始状态继续执行
几个要点:
- 用 proj.hook() hook 序言块的最后一条指令地址,让 angr 直接从真实块地址开始执行
- 对于每个真实块,用 angr 的模拟器(simgr)单步执行,如果执行流跳转到的地址在 real_blocks 里就认为这是后继块
- 对于符合的普通无条件跳转,直接记录;对于 CSEL 条件跳转,强制选择 CSEL 的某个分支结果,而不用依赖当前状态里的条件标志,分别模拟真/假两种情况
具体实现
- CSEL 指令解析以及它的特殊处理机制
csel x0, x1, x2, eq
1 | |
1 | |
- 识别真实块的后继
从初始化 state 出发,找到进入该 real_block 的 state,然后在该 block 上判定是无条件还是遇到 CSEL 需要分支处理,并把结果写入 path
主要流程:
创建一个主模拟器开始执行,遍历所有 active 状态寻找真实块
复制当前状态创建新模拟器用于探索后继块,同时单步执行一次避免状态混淆
无条件跳转的情况下,如果有多个路径同时执行到真实块,排除掉 ret 块的路径
CSEL 条件跳转的情况下,我们知道 angr 在默认执行时,会依据当前状态的条件标志决定走哪一边,但这里采用半符号执行,不依赖真实标志,所以复制一份当前状态(True 分支),强制设定 csel 结果为真分支,再复制一份(False 分支),强制设定为假分支,然后执行直到遇到属于 real_blocks 的真实块地址
1 | |
- 主流程
初始化 angr
1 | |
构造 path 字典,key 是每个真实块地址,value 是该块的后继真实块列表
1 | |
取主序言的最后一条指令,后面要在这个位置 hook 来修改 PC 跳转,直接跳到某个真实块
1 | |
遍历真实块地址,检查是否属于某个子序言块
1 | |
hook 函数
1 | |
最后就是调用 find_block_succ 获取后继块并输出控制流关系
重建控制流
关键点:
对于条件分支块 (在 patch_list 中有两个后继块): 查找 CSEL 指令,然后使用 keystone 汇编器生成一条条件跳转指令 (B.cond) 和一条无条件跳转指令 (B),并用它们替换 CSEL 指令和块末尾的指令
对于无条件跳转块 (在 patch_list 中有一个后继块): 在该块的末尾打上一个无条件跳转 (B) 指令,使其直接跳转到正确的目标块
对于返回块 (在 patch_list 中没有后继块): 跳过,不进行任何修改
1 | |